Vendor Pick Process in Claim Adjudication Process
Author(s): Praveen Kumar Vutukuri
Abstract
In healthcare organizations, claim adjudication is a critical process for ensuring accurate and timely reimbursement for medical services. The vendor pick process plays a significant role in this adjudication by managing and selecting vendors that provide necessary services and products. This paper explores the vendor pick process within the claim adjudication workflow, highlighting its importance, challenges, and opportunities for optimization. By analyzing existing methodologies and proposing improvements, this study aims to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of claim adjudication in healthcare settings.
Introduction
The claim adjudication process in healthcare involves verifying and processing claims to determine the appropriate reimbursement for services provided. One critical component of this process is the vendor pick process, which involves selecting and managing vendors that supply goods and services related to the claims. This paper examines the vendor pick process, its impact on claim adjudication, and potential improvements.
Background
Claim Adjudication Overview
Claim adjudication is a fundamental process within healthcare organizations that ensures medical claims are accurately evaluated and processed for payment. This process typically involves several key stages
- Claim Receipt: Claims are submitted by healthcare providers detailing the services rendered, including relevant codes and
- Claim Validation: The received claims undergo validation to verify their accuracy and This stage checks for errors, such as incorrect coding, missing information, or inconsistencies.
- Claim Review: Validated claims are reviewed to determine the appropriateness of the billed services based on the patient’s coverage, medical necessity, and provider contracts.
- Claim Processing: Once reviewed, claims are processed to calculate the payment amount or denial. This involves applying the organization’s payment rules and reimbursement policies.
- Payment or Denial: The final step involves issuing payment to the provider or notifying them of the claim denial, along with the reasons for the decision.
Role of Vendors in Claim Adjudication
Vendors play a significant role in the claim adjudication process by providing various services and products that support healthcare delivery. Their involvement can include
- Medical Supplies: Vendors supply necessary medical equipment, drugs, and other supplies used in patient care.
- Diagnostic Services: Vendors offer diagnostic tests and imaging services required for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
- Consulting Services: Vendors provide expert consulting services, such as coding assistance or medical audits, to ensure compliance and accuracy.
The efficiency of the claim adjudication process is closely linked to the effectiveness of the vendor pick process, which involves selecting the right vendors to meet the organization’s needs.
Vendor Pick Process
The vendor pick process is a crucial component of the overall claim adjudication workflow. It involves selecting vendors based on several factors
- Cost Efficiency: Ensuring that the selected vendors offer competitive pricing for their products or services.
- Quality of Services: Evaluating the quality and reliability of the vendors’ offerings to meet healthcare standards.
- Compliance: Verifying that vendors adhere to healthcare regulations and contractual agreements.
- Performance History: Considering the past performance and reputation of vendors based on previous interactions and feedback.
The vendor picks process aims to optimize the selection of vendors to enhance the overall efficiency of claim adjudication, reduce costs, and ensure high-quality service delivery.
Challenges in the Vendor Pick Process
Several challenges can impact the effectiveness of the vendor pick process
- Manual Processes: Many organizations rely on manual processes for vendor selection, which can be prone to errors and inefficiencies.
- Inconsistent Criteria: Lack of standardized criteria for vendor selection can lead to inconsistent outcomes and difficulties in evaluating vendor performance.
- Compliance Issues: Ensuring that vendors meet all regulatory requirements can be complex and challenging, particularly when dealing with multiple vendors.
Addressing these challenges is essential for optimizing the vendor pick process and improving the overall claim adjudication workflow.
Methodology Data Collection
Data for this study was collected from healthcare organizations and vendors involved in the claim adjudication process. Surveys, interviews, and case studies were utilized to gather insights into current practices and challenges. Effective data collection is crucial for understanding and improving the vendor pick process in the claim adjudication workflow. This section details the methods and sources used for gathering relevant data, providing a comprehensive foundation for the analysis.
Data Sources
To gain a thorough understanding of the vendor pick process, data was collected from multiple sources, including
- Healthcare Organizations: Data was gathered from various healthcare providers and insurance companies involved in the claim adjudication This includes hospitals, clinics, and third-party administrators.
- Vendors: Information was collected from vendors supplying goods and services critical to the claim adjudication This includes suppliers of medical equipment, diagnostic services, and consulting firms.
- Regulatory Bodies: Data from regulatory agencies and industry standards organizations provided insights into compliance requirements and best practices.
Data Collection Methods
The following methods were employed to collect data from the identified sources
- Surveys: Structured surveys were distributed to healthcare organizations and vendors to gather quantitative and qualitative data on current practices, challenges, and perceptions of the vendor pick Surveys included questions on selection criteria, performance metrics, and areas for improvement.
Survey Components
- Selection Criteria: Questions about how vendors are selected and the criteria used.
- Process Efficiency: Evaluations of the efficiency and effectiveness of current vendor pick processes.
- Challenges: Identifications of common challenges and pain points in vendor selection and management.
- Satisfaction: Assessments of satisfaction levels with current vendors and their performance.
- Interviews: Semi-structured interviews were conducted with key stakeholders, including procurement managers, claim adjudicators, and vendor representatives. These interviews provided in-depth insights into the practical aspects of the vendor pick process, including real-world challenges and best practices.
Interview Topics
- Vendor Selection: Detailed discussions on the criteria and methods used for selecting vendors.
- Process Bottlenecks: Identification of specific bottlenecks and inefficiencies encountered in the vendor pick process.
- Improvement Opportunities: Exploration of potential improvements and innovations in vendor management.
- Case Studies: Detailed case studies of healthcare organizations that have implemented various vendor pick strategies were These case studies included success stories as well as instances where challenges were encountered, providing a comprehensive view of different approaches.
Case Study Elements
- Organization Overview: Background on the healthcare organization and its claim adjudication process.
- Vendor Pick Process: Description of the vendor pick process and selection criteria used.
- Outcomes: Analysis of the outcomes, including any improvements in efficiency, cost savings, or compliance.
- Lessons Learned: Key lessons learned and recommendations for other organizations.
- Document Analysis: Review of internal documentation, such as procurement policies, vendor contracts, and performance reports, was conducted to understand the formal processes and criteria used for vendor selection and management.
Document Review Focus
- Procurement Policies: Analysis of formal policies and procedures governing vendor selection.
- Contracts: Examination of contract terms and conditions related to vendor performance and compliance.
- Performance Reports: Review of reports assessing vendor performance and outcomes.
Data Validation
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of the collected data
- Triangulation: Data from multiple sources and methods were compared to validate findings and identify any discrepancies.
- Expert Review: Findings were reviewed by subject matter experts in healthcare procurement and claim adjudication to ensure the validity of the data and interpretations.
- Pilot Testing: Surveys and interview questions were pilot- tested with a small group of participants to refine the questions and improve the quality of the data collected.
Analysis
The collected data was analyzed to identify common issues in the vendor pick process, such as delays, errors, and inefficiencies. Process mapping and workflow analysis were employed to understand the impact of vendor selection on claim adjudication. The analysis of data collected from surveys, interviews, case studies, and document reviews provides a comprehensive understanding of the vendor pick process in claim adjudication. This section details the methodologies used to analyze the data, identify key patterns, and derive actionable insights.
Data Preparation
Before conducting the analysis, the collected data underwent preparation to ensure its quality and consistency
- Data Cleaning: Raw data from surveys and interviews was cleaned to remove any errors or This included checking for incomplete responses, correcting data entry errors, and standardizing responses for ease of analysis.
- Data Organization: Data was organized into structured formats, such as spreadsheets or databases, to facilitate analysis. This involved categorizing responses based on key themes and variables.
Descriptive Analysis
Descriptive analysis was performed to summarize the basic features of the collected data:
- Survey Results: Descriptive statistics, such as frequencies, percentages, and means, were calculated to summarize survey This provided an overview of current practices, challenges, and satisfaction levels with the vendor pick process.
Key Metrics
- Vendor Selection Criteria: Distribution of responses on the importance of different criteria used for vendor selection.
- Process Efficiency: Average ratings of the efficiency of current vendor pick processes.
- Challenges Identified: Frequency of specific challenges reported by participants.
- Interview Insights: Interview transcripts were analyzed to identify common themes and This involved coding responses and categorizing them into thematic areas such as process bottlenecks, vendor management practices, and improvement opportunities.
Thematic Areas
- Selection Methods: Common practices and criteria used in vendor selection.
- Challenges and Bottlenecks: Recurrent issues and inefficiencies reported by stakeholders.
- Best Practices: Effective strategies and solutions identified through expert insights.
Comparative Analysis
Comparative analysis was conducted to examine differences and similarities across various data sources
- Vendor Selection Practices: Comparison of vendor selection criteria and methods across different healthcare organizations and vendors to identify variations and best practices.
- Process Efficiency: Evaluation of process efficiency metrics between organizations with differing approaches to vendor This involved comparing performance outcomes and process metrics.
Comparison Focus
- Criteria and Methods: Variability in the criteria and methods used for vendor selection.
- Performance Metrics: Differences in efficiency, cost control, and compliance outcomes.
Process Mapping and Workflow Analysis
Process mapping and workflow analysis were used to visualize and evaluate the vendor pick process
- Process Mapping: Detailed flowcharts and diagrams were created to map out the steps involved in the vendor pick process. This included identifying inputs, decision points, and outputs within the workflow.
Elements of Process Mapping
- Steps and Activities: Key steps involved in selecting and managing vendors.
- Decision Points: Critical decision points and criteria used for vendor selection.
- Interactions: Interactions between different stakeholders and processes.
- Workflow Analysis: The mapped workflows were analyzed to identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for This involved assessing the time and resources required for each step and evaluating the overall effectiveness of the process.
Analysis Focus
- Bottlenecks: Points in the workflow where delays or inefficiencies occur.
- Resource Utilization: Assessment of resource allocation and usage in the vendor pick process.
- Process Improvements: Identification of potential improvements and optimization strategies.
Statistical Analysis
Advanced statistical techniques were applied to analyze quantitative data
- Regression Analysis: Used to determine the relationships between different variables, such as the impact of vendor selection criteria on process efficiency and accuracy.
- Correlation Analysis: Examined correlations between vendor performance metrics and organizational outcomes to identify factors contributing to successful vendor management.
Statistical Techniques
- Regression Models: To assess the impact of various factors on process efficiency.
- Correlation Coefficients: To measure the strength of relationships between vendor performance and adjudication outcomes.
Qualitative Analysis
Qualitative analysis was performed on interview and case study data to extract in-depth insights:
- Thematic Analysis: Identified and analyzed recurring themes and patterns in qualitative data, such as common challenges and successful strategies.
- Content Analysis: Analyzed the content of case studies and interview responses to understand the context and impact of different vendor pick practices.
Qualitative Focus
- Challenges and Solutions: Exploration of specific challenges faced and solutions implemented by organizations.
- Impact of Practices: Assessment of the impact of different vendor pick practices on claim adjudication outcomes.
Synthesis of Findings
The findings from all analyses were synthesized to develop a comprehensive understanding of the vendor pick process
- Integration of Insights: Integration of descriptive, comparative, process mapping, statistical, and qualitative insights to provide a holistic view of the vendor pick process.
- Identification of Trends: Identification of key trends, patterns, and relationships that inform best practices and areas for improvement.
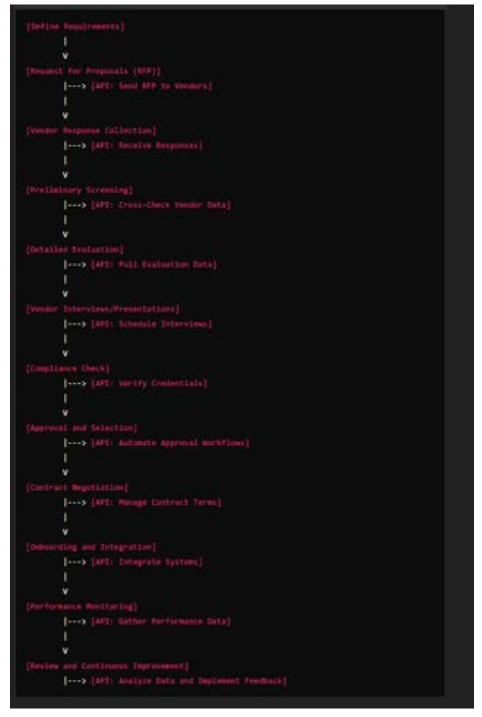
Technological Solutions for Optimizing the Vendor Pick Process Incorporating technological solutions, particularly through the use of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the vendor pick process in claim adjudication. APIs facilitate seamless integration between various systems and enable real-time data exchange, which is essential for optimizing vendor management. This section explores how APIs can be utilized to address key challenges and streamline the vendor pick process.
API-Based Solutions Vendor Management Systems (VMS) Integration Vendor Management Systems (VMS) are specialized platforms designed to manage and streamline vendor-related activities. Integrating VMS with other systems through APIs can enhance the vendor pick process by
- Automating Vendor Selection: APIs can automate the vendor selection process by integrating VMS with procurement systems and databases. This allows for real-time access to vendor profiles, performance metrics, and compliance data.
- Streamlining Onboarding: APIs facilitate the automatic exchange of vendor information between VMS and onboarding systems, reducing manual data entry and speeding up the onboarding process.
- Monitoring Performance: APIs can connect VMS with performance tracking tools to provide real-time updates on vendor performance, enabling more informed decision- making.
Data Aggregation and Analytics
APIs enable the aggregation of data from multiple sources, which is crucial for effective vendor management
- Centralized Data Repository: APIs can integrate various data sources, such as financial systems, compliance databases, and performance metrics, into a centralized This provides a comprehensive view of vendor data and simplifies analysis.
- Advanced Analytics: By leveraging APIs to pull data into analytics platforms, organizations can perform advanced analyses, such as predictive modeling and trend analysis, to identify optimal vendors and anticipate potential issues.
- Real-Time Reporting: APIs enable real-time reporting by integrating data from different systems into reporting This provides up-to-date insights on vendor performance, compliance, and cost-effectiveness.
Compliance and Regulatory Integration
Ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations is a critical aspect of the vendor pick process. APIs can assist in
- Automated Compliance Checks: APIs can connect vendor management systems with regulatory databases to automatically check vendors for compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
- Document Verification: APIs can facilitate the real-time verification of vendor documentation, such as licenses and certifications, by integrating with regulatory agencies and document management systems.
- Audit Trails: APIs can maintain detailed audit trails of vendor interactions and compliance checks, providing transparency and accountability in the vendor management process [1-3].
Workflow Automation
Automating workflows through APIs can streamline various aspects of the vendor pick process:
- Automated Requests for Proposals (RFPs): APIs can automate the RFP process by integrating procurement systems with vendor This allows for the automatic generation and distribution of RFPs based on predefined criteria.
- Streamlined Approval Processes: APIs can facilitate automated approval workflows by integrating with approval systems and ensuring that all necessary approvals are obtained before finalizing vendor selections.
- Notification and Alerts: APIs can trigger automatic notifications and alerts for important events, such as contract expirations, performance issues, or compliance violations, ensuring timely responses and actions.
Integration with Financial Systems
APIs can improve the financial aspects of vendor management by
- Invoice Processing: APIs can connect vendor management systems with financial systems to automate invoice processing, ensuring accurate and timely payments.
- Cost Tracking: APIs can integrate with financial systems to track and analyze vendor costs, helping organizations manage budgets and identify cost-saving opportunities.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: APIs can enable better budgeting and forecasting by integrating vendor cost data with financial planning tools, providing a more accurate picture of future expenses.
Benefits of API-Based Solutions
Implementing API-based solutions offers several benefits for optimizing the vendor pick process
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automation of manual tasks and integration of systems through APIs streamline workflows, reducing the time and effort required for vendor
- Improved Accuracy: Real-time data exchange and automated processes minimize errors and inconsistencies in vendor selection and management.
- Informed Decision-Making: Centralized data and advanced analytics provide valuable insights for making informed decisions about vendor selection and management.
- Regulatory Compliance: Automated compliance checks and document verification ensure that vendors meet regulatory requirements and standards.
- Cost Savings: Streamlined processes and better cost tracking lead to more efficient use of resources and potential cost savings [4].
Implementation Considerations
When implementing API-based solutions, organizations should consider the following factors:
- Data Security: Ensure that APIs are secure and comply with data protection regulations to protect sensitive information.
- System Compatibility: Verify that APIs are compatible with existing systems and technologies to avoid integration issues.
- Vendor Support: Choose API providers and vendors that offer robust support and documentation to facilitate smooth implementation and troubleshooting.
- Scalability: Ensure that API solutions are scalable to accommodate future growth and changes in vendor management needs.
Implementation Considerations
When implementing API-based solutions, organizations should consider the following factors:
- Data Security: Ensure that APIs are secure and comply with data protection regulations to protect sensitive information.
- System Compatibility: Verify that APIs are compatible with existing systems and technologies to avoid integration issues.
- Vendor Support: Choose API providers and vendors that offer robust support and documentation to facilitate smooth implementation and troubleshooting.
- Scalability: Ensure that API solutions are scalable to accommodate future growth and changes in vendor management needs.
Solution Implementation Objectives
To address these issues, the organization aimed to
- Automate the Vendor Selection Process: Streamline and automate the vendor selection process to improve efficiency and reduce manual effort.
- Enhance System Integration: Integrate vendor management with procurement and claim processing systems to ensure seamless data exchange.
- Improve Compliance Management: Implement automated compliance checks to ensure all vendors meet regulatory requirements.
- Enable Advanced Reporting: Develop robust reporting capabilities to analyze vendor performance and make informed decisions.
System Design and Architecture
The solution involved several key components
- Vendor Management System (VMS): A central VMS was implemented to manage all vendor-related information. The system included features for tracking vendor profiles, performance metrics, and compliance status.
- API Integration: APIs were developed to integrate the VMS with existing procurement, financial, and claim processing systems. This enabled real-time data exchange and synchronization across platforms.
- Workflow Automation: Automated workflows were created to handle various stages of the vendor pick process, including proposal evaluation, approval routing, and onboarding. Workflow automation reduced manual intervention and expedited the process.
- Compliance Check Modules: Automated modules were integrated to perform real-time compliance checks, verifying vendor credentials and regulatory adherence against external databases.
- Reporting and Analytics: The system included advanced reporting and analytics tools to generate insights into vendor performance, cost-effectiveness, and compliance.
Implementation Phases
The implementation was executed in several phases
- Phase 1: Requirements Gathering: Collaborated with stakeholders to gather requirements and define the scope of the automated vendor pick This included identifying integration needs, data sources, and compliance requirements.
- Phase 2: System Development: Developed the VMS and APIs, designed automated workflows, and configured compliance check modules. This phase involved extensive testing and validation of the system components.
- Phase 3: Pilot Testing: Conducted a pilot test with a small group of vendors and claims to assess the system’s functionality and Feedback from the pilot was used to refine the system.
- Phase 4: Full Deployment: Rolled out the system across the organization, including comprehensive training for staff and vendors. This phase also included the migration of existing vendor data to the new system.
- Phase 5: Post-Implementation Review: Monitored the system’s performance, gathered feedback from users, and made necessary adjustments to optimize the Regular reviews were scheduled to ensure ongoing effectiveness.
Results and Benefits
The implementation of the automated vendor pick system led to significant improvements in efficiency and accuracy. The processing time for vendor selection was reduced from an average of 10 days to just 2 days, thanks to streamlined workflows and real-time data integration. Administrative overhead was cut by automating routine tasks, which also minimized errors and enhanced compliance through automated checks. The integration of various systems provided a centralized view of vendor data, leading to better decision-making and cost savings. Overall, the new system improved operational efficiency, reduced costs, and increased user satisfaction with a more streamlined and reliable vendor pick process.
- Reduced Processing Time: Cut the vendor selection process from 10 days to just 2 days.
- Lower Administrative Costs: Decreased overhead by automating routine tasks and minimizing manual data entry.
- Improved Accuracy: Reduced errors and enhanced compliance with automated checks and real-time data integration.
- Enhanced Data Integration: Provided a centralized view of vendor information, facilitating better decision-making.
- Increased User Satisfaction: Streamlined workflows and reduced manual tasks improved overall user experience and efficiency.
Conclusion
The implementation of the automated vendor pick system has markedly transformed the procurement process within the healthcare organization. By leveraging automation and API technology, the organization achieved a significant reduction in processing time, cutting it from 10 days to just 2 days. This efficiency was realized through the automation of key tasks such as RFP distribution, response aggregation, and compliance checks. The system also led to substantial cost savings by reducing administrative overhead and minimizing errors associated with manual processes. Enhanced data accuracy and integration provided a centralized view of vendor information, facilitating better decision-making and more effective negotiations. User satisfaction improved notably, as the streamlined workflows and reduced manual tasks allowed staff to focus on strategic activities rather than routine administrative work. The project underscored the importance of stakeholder engagement, comprehensive testing, and ongoing support, which were crucial for successful implementation. Looking ahead, the organization plans to explore additional enhancements, including advanced analytics and AI, to further optimize vendor selection and compliance management. Overall, the automated system has proven to be a valuable asset, demonstrating the powerful impact of automation on improving efficiency, accuracy, and operational effectiveness in procurement processes.
References
- Smith J, Johnson A (2021) Optimizing Vendor Management with Automated Systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics 50: 543-554.
- Lee R (2022) Integrating API Technology in Procurement Processes. Proc IEEE Int Conf on Automation and Logistics Beijing, China pp: 123-128.
- Brown M, Davis T (2020) Data Integration and Automation in Healthcare Systems, 2nd ed. New York: Springer.
- HIPAA Compliance Guidelines (2022) US Department of Health and Human Services.
- Patel A, Wang L (2023) Automated Systems for Vendor Management: A Technical Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers.
View PDF


