Author(s): Nikhil Jarunde
The burgeoning international derivatives market demands a more unified approach to regulation. Current inconsistencies across jurisdictions create significant compliance burdens for firms, hindering market efficiency and financial stability. This paper explores the potential of fintech solutions to bridge this gap. By examining the challenges of cross-border derivatives compliance, we analyze how innovative technologies can streamline reporting, automate risk management, and enhance data standardization. The paper argues that fintech can be a powerful tool for facilitating global regulatory harmonization, promoting transparency and mitigating systemic risk in the derivatives market.
The derivatives market plays a crucial role in global finance, enabling risk management and facilitating price discovery. However, its international character is challenged by a fragmented regulatory landscape. Each jurisdiction enforces its own set of rules for derivatives trading, leading to a complex web of compliance requirements for firms operating across borders. This disparity creates inefficiencies, increases costs, and hinders market participation. More importantly, inconsistencies in regulatory frameworks can pose systemic risks, as loopholes in one jurisdiction can potentially undermine the stability of the entire market.
This paper investigates the potential of financial technology (fintech) to address the challenges of cross-border derivatives compliance. Fintech encompasses a broad range of technological innovations applied to the financial sector. By leveraging advancements in areas like data analytics, distributed ledger technology (blockchain), and artificial intelligence, fintech solutions can offer a path towards streamlining compliance processes and fostering greater harmonization in the global derivatives market. The following sections will explore the specific challenges faced by firms and how fintech can be utilized to:
The global derivatives market encompasses a wide variety of financial instruments, including futures, options, swaps, and structured products. These instruments are traded across several major global exchanges, like the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME), London Stock Exchange (LSE), and Shanghai Futures Exchange, as well as through Over-the-counter (OTC) transactions. The derivatives market is vast and highly leveraged, with the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) estimating the total notional amounts outstanding to be in the hundreds of trillions of dollars. Figure 1 below is a line graph showing the growth of total notional value of outstanding derivatives from 2000 to 2020, highlighting the market’s increasing size. Figure 2 is a pie-chart illustrating the breakdown of derivatives by asset classes in 2022, demonstrating the diverse nature of the market.
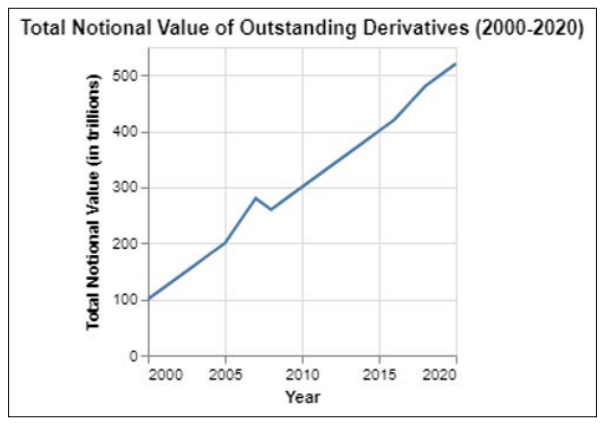
Figure 1: Growth of Total Notional value of Outstanding Derivatives (2000–2020)
The disparate regulatory frameworks result in significant compliance costs for firms. These include operational costs related to adapting systems and processes to accommodate different reporting and clearing requirements, legal costs in understanding and navigating multiple regulatory environments, and ongoing costs in maintaining compliance. Such burdens can be particularly heavy for smaller market participants, potentially reducing their competitiveness and ability to innovate. Below is a bar chart illustrating the comparison of operational spending devoted to compliance in 2022 for firms across regions with stricter versus more lenient regulations.
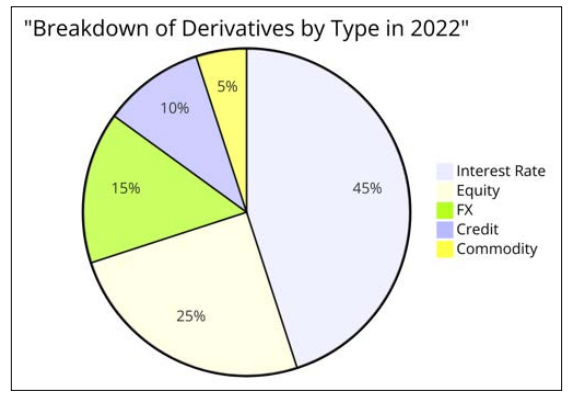
Figure 2: Pie Chart Representing Breakdown of Derivatives by Asset Classes (2022)
Major players in this market include institutional investors, hedge funds, banks, and other financial institutions. These entities use derivatives for various purposes such as hedging risk, speculating on future price movements, and arbitraging price discrepancies between different markets.
The derivatives market poses significant systemic risks due to its complexity and interconnectedness. One major risk is market risk, where extreme volatility can lead to large losses. Credit risk also looms large, as the failure of one party to meet its obligations could impact numerous other parties due to the interconnected nature of these contracts.
Cross-border trading adds another layer of complexity and risk. Different countries’ legal systems and market practices can lead to disputes over jurisdiction and applicable laws in the event of a default or other issues. Counterparty risk is also a critical concern, especially in the OTC markets where the failure of a single major player can have ripple effects throughout the financial system.
Regulatory regimes for derivatives vary significantly across different jurisdictions, leading to a fragmented landscape that can pose challenges for international market participants. In the United States, the Dodd-Frank Act requires comprehensive reporting and clearing for most derivatives, aimed at increasing transparency and reducing systemic risk. The European Market Infrastructure Regulation (EMIR) serves a similar purpose in the EU, mandating reporting, clearing, and risk mitigation standards.
Asia-Pacific features a diverse regulatory environment; countries like Japan and Australia have robust regulatory frameworks, whereas emerging markets are often less regulated. This variation affects everything from how derivatives are reported and cleared to how risk management is enforced, creating a complex environment for firms that operate globally. Below is a graph diagram illustrating the distribution of regulatory frameworks in major regions of the world, visually emphasizing the lack of global uniformity.
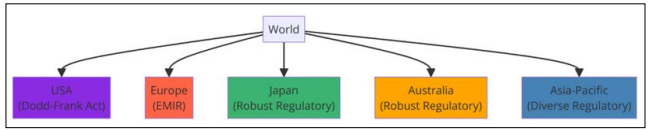
Figure 2: Regulatory Frameworks in Major Regions of the World
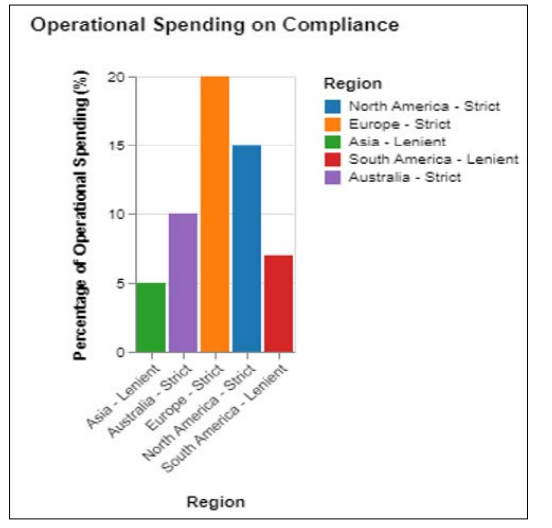
Figure 3: Bar Chart for Percentage of Operational Spending on Compliance Across Different Regions
The need for robust risk management systems further increases operational costs. Firms must invest in technology and skilled personnel to manage the risks associated with their derivatives trading effectively, from market and credit risk to legal and reputational risks in different jurisdictions.
Fintech, traditionally seen as a disruptor in the financial sector, has evolved to play a crucial role in enhancing and streamlining financial operations, especially in compliance and regulatory adherence. Beyond simplifying transactions and financial services, fintech now encompasses a broad range of compliance-specific technologies designed to tackle the complexities of regulatory demands globally. These technologies are not just about disruption; they represent an integral support system for financial institutions, ensuring they stay ahead of regulatory changes while maintaining operational efficiency. Figure 4 below is a mind map diagram illustrating the Fintech Ecosystem Overview, highlighting various sectors impacted by fintech including banking, insurance, investments, and compliance technologies.
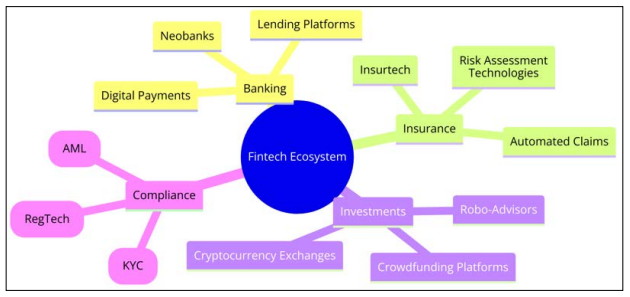
Figure 4: Fintech Ecosystem Overview
Moreover, as per a 2023 report from Thomson Reuters Regulatory Intelligence (TRRI), Institutions utilizing fintech for compliance purposes reported significantly lower costs in 2022 compared to their counterparts. This highlights the potential for substantial cost savings through fintech adoption, specifically in the realm of regulatory compliance. Figure 5 below is a bar graph that demonstrates a clear difference in average compliance costs between financial institutions in 2022 that have adopted fintech solutions and those that haven’t.
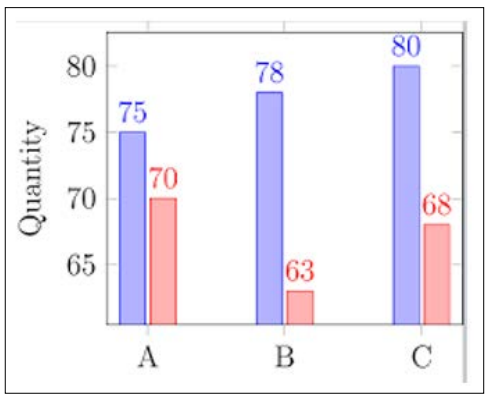
Figure 5: Bar graph for Average compliance costs for financial institutions With Fintech (Blue) Vs Without Fintech (Red)
Fintech significantly enhances the ability of financial institutions to manage large volumes of data, making it a vital tool for compliance with diverse and stringent regulatory frameworks.
In risk management, fintech provides tools that offer not only real-time monitoring but also predictive capabilities to foresee potential risks and mitigate them proactively.
Effectiveness and Benefits: Such tools enable financial institutions to maintain a constant overview of their risk landscape and adjust their strategies dynamically to align with both market conditions and regulatory requirements. This proactive approach to risk management not only ensures compliance but also secures the institution’s assets against unforeseen vulnerabilities.
DLT has shown considerable promise in increasing transparency and enhancing trust in financial transactions, which is pivotal for compliance and regulatory reporting. One of the most promising applications of DLT in fintech is the creation of shared, tamper- proof trade repositories or reporting platforms. These platforms can serve as a single source of truth for transactional data, accessible by regulators and participants alike, ensuring consistency and immutability of records.
For instance, a DLT-based reporting platform could automatically and securely record trades, confirmations, and settlements. This would drastically reduce the likelihood of disputes and fraud, as all parties would have access to the same unalterable records. Moreover, such platforms could facilitate faster regulatory reporting and easier compliance checks, as data would be immediately available and verifiable in real-time, reducing the need for complex reconciliations. Below is an illustrative image showing a Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) network, highlighting nodes, the decentralized nature, and areas where compliance data is recorded and verified. This visual helps explain how DLT provides a secure, transparent, and immutable platform for financial transactions and regulatory compliance.
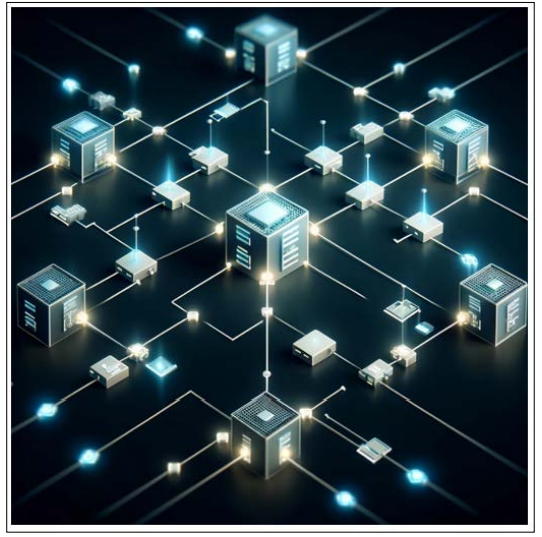
Figure 6: Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
Efforts to harmonize financial regulations have been ongoing, particularly following the global financial crisis of 2008, which highlighted the need for a coordinated international approach to financial regulation. Significant initiatives include those by the Group of Twenty (G20), which has been at the forefront in calling for global financial reforms, including the regulation of derivatives markets, enhancing transparency, and improving risk management practices across borders.
The International Swaps and Derivatives Association (ISDA) has also played a critical role, particularly in standardizing contracts and operational procedures in the derivatives markets to reduce systemic risk. ISDA’s work has been instrumental in creating frameworks that reduce legal and operational uncertainties.
Furthermore, major financial stability bodies such as the Financial Stability Board (FSB) and the International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) have worked towards global standards that address vulnerabilities in the financial system, promoting the resilience of financial institutions and markets.
Harmonization of financial regulations offers several key benefits:
Despite these benefits, several challenges impede the harmonization of financial regulations:
This paper has extensively discussed the instrumental role fintech can play in transforming the regulatory landscape of the global derivatives market. As we have seen, the derivatives market, while crucial for risk management and price discovery in global finance, is currently hampered by a fragmented regulatory framework. This fragmentation not only elevates compliance costs but also introduces systemic risks that could potentially destabilize the global financial system.
Through the application of fintech solutions-encompassing advanced data analytics, distributed ledger technology (DLT), and artificial intelligence-we have identified pathways through which these technologies can significantly streamline cross- border derivatives compliance. Fintech’s capability to automate complex reporting processes, enhance risk management practices, and standardize data formats presents a compelling case for its adoption as a central element in the push towards regulatory harmonization.
Furthermore, the implementation of these technologies promises not only to reduce the operational burdens on financial institutions but also to enhance the transparency and efficiency of the derivatives market. By facilitating a more unified regulatory approach, fintech stands as a catalyst for mitigating systemic risk and fostering a stable, efficient market environment.
In conclusion, as the derivatives market continues to evolve and expand, the need for a coordinated regulatory approach becomes more apparent. Fintech offers practical solutions that can bridge the current gaps in regulatory practices, paving the way for a more integrated and resilient global financial landscape. Moving forward, it will be crucial for policymakers, regulators, and market participants to foster an environment that encourages the adoption of these technologies, ensuring that the global derivatives market can fully leverage the potential of fintech to meet the challenges of the 21st century [1-9].
