Author(s): Pranith Shetty
Financial Services sector are a very critical part of nation’s infrastructure, cyberattacks on this sector could potentially have devastating consequences on the economy. Cyber and information security landscape are continuously evolving thus putting a lot of pressure on the systems responsible for operations. System and business owners are also cornered from all directions in terms of Audits, Assessments and compliance matters, thus making it difficult to deliver on business objectives, time and resourcing constraints have also played a contributing role. Security field has varied staff members with different skills and area of expertise, Information security management is one such skillset that needs to be housed in every financial firm and other sectors. Information Security Managers have the expertise to bridge the gap between not only Systems owners and Security experts, Compliance staff but also with Business. They can work in advisory capacity, guiding security risks through the Risk management Lifecyle towards mitigation, reporting becomes comparatively easier with them in the fold. They can also quarterback or in other words run point on Compliance related initiatives. This article helps understand the Information (cyber) security landscape in the financial services sector and the role information security managers can play to help relieve the burden on system owners and security SMEs (Subject Matter experts) to help balance the scales in business’s favor.
Financial Services sector are a very vital component of our nation’s critical infrastructure. Large scale cyberattacks, power outages and natural calamities like flood, earthquakes are the potential risks to this sector [1]. Financial services includes investment banks, insurance firms and other critical financial utilities. Institutions like big banks , retail, credit unions also fold into this sector by definition. As we did experience in 2008, a crisis in this sector caused a widespread collapse across the globe so it’s very important to protect this sector from the various Cybersecurity threats and Information security related risks.
Information Security Managers are primarily responsible for the smooth functioning of the Information Security program, system, governance etc [2]. They are also alternatively called as Information security officers, Cybersecurity analysts, Security specialists and so on. The role description depends on the hiring organization’s needs, functions, org structure etc.
Depending on the line of defense meaning if the officer is in 1 st line working with engineers, the portfolio of work would differ as compared to the officer in 2nd line working on operational risks and governance related functions but overall Information Security managers are in consulting / advisory capacity that requires them to advise engineers on risk security remediations, they also advise leadership/senior management on risks that cannot be remediated and need to be accepted. They recommend all sorts of measures proactive, reactive that act in the favor of the firm.
NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) recognizes both these areas as different in terms of domains, there is a slight variance as described here, but in reality Cybersecurity is a subset of Information security as described below, CIA tenets here means Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability which form the basis of Information security as a domain, Cybersecurity on the other hand is narrowed to the use of computer systems, cell phones etc.
So in essence an Information Security Manager would also be responsible for Cybersecurity relates issues and risks, in some instances firms hire exclusively for Cybersecurity roles.

Stakeholders, Engineers, Business owners and system owners in financial services are from varied backgrounds, some are application owners while some are system owners, database admins, as a result they need a staff member; who has the background and expertise in dealing with information security and risks, this member can work with the potential risk owners in ensuring the findings from audit teams or assessment teams make sense. There are instances where audit teams would create findings outside the scope of Audit. There are findings that are attributed to target dates that are very close, without proper estimations. The system owners out of obligation accept those target dates and eventually end up with misplaced priorities. They could have worked on building products or improving processes to drive business as opposed to working on remediations that could have had an extended date based on the risk rating or could have been a finding beyond the scope of audit unfairly tagged. There are cases where Business / System owners have to attend multiple assessments as part of the accountable team, they could easily delegate these meetings to their information security managers; who can run point and work with these owners on streamlining Information Security programs.
This government website explains in detail the various core competencies that the Information Security Manager brings onto the table and indirectly helping us understand the positives of this role [2].
This thought leadership article from Safebreach, a consulting firm helps us understand the strain that Security and It teams are in at the moment to ensure secure cybersecurity defenses [3].
There are various articles that discuss the need to have cybersecurity controls for protecting financial and customer data [4,5].
There are several reasons why financial services sector should take cybersecurity seriously, since these firms are very important and classified as critical national infrastructure a threat to these firms can have a devastating impact across different sectors and can span across nations globally [4,6]. Some of the few repercussions of not having cybersecurity measures in place are: Financial Impact: Any data breach resulting from insider or external attack could result in loss of digitized transactions, impacting annual revenue, profits, financial statements.
Reputational Impact: As a result of the breach, faith in the institutions will be questioned by both existing and potential customers.
Regulatory Impact: Failure to safeguard public interests, data etc., additionally noncompliance to the regulatory laws could result in fines and affect the overall operations of the firm.
Hence it’s important to ensure necessary Information Security controls for Protection of customer data, Prevention of financial fraud, Compliance with regulatory requirements and protection of intellectual property.
Firms are investing in Cybersecurity or will continue to invest because the number of threats and attacks are only going to increase and evolve, being proactive will eventually pay its benefits, Investing now can save the firms approx. 4.45 million$, using AI (Artificial Intelligence) along with cybersecurity measures would result in more savings and improve the risk and control posture twofold [7].
Firms with a robust incident response framework saved an average of 2 million $.
Along with investing in technologies and framework, it’s also important for firms to assess themselves against industry wide compliance frameworks and regulations such as GDPR, FINRA etc. since noncompliance may result in extensive fines and reputational impact along with loss of customer faith and trust.
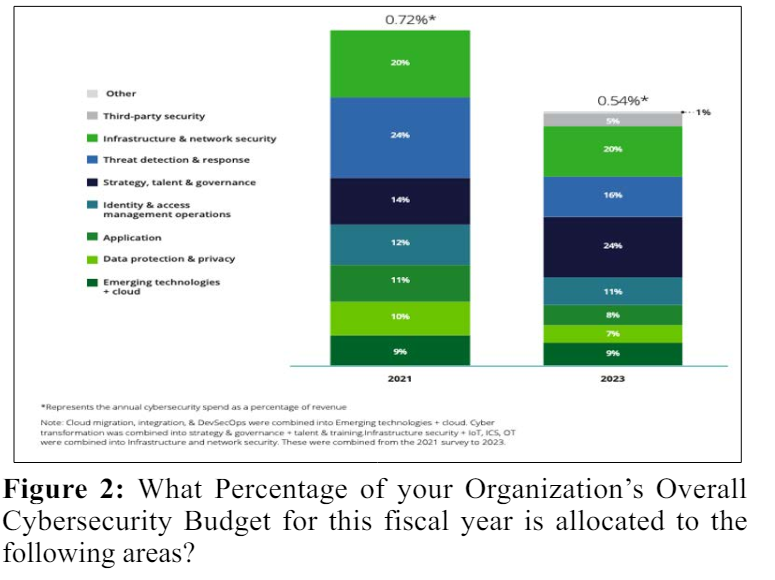
Below are some statistics and visuals that draw comparisons between different sectors in financial services and within a financial firm, where is the overall cybersecurity budget being diverted to? [8].

In any firm including financial services, there are several risk identification channels such as
Risk control self-assessments, this is a self-identification of risks process that the control owners, systems owners, risk owners have to attest to.
Technology control assessments which checks for the maturity of system controls and ensures there are no control gaps, this is operated by the operational risk team in 2nd line of defense. There are some assessments operating out of second line, mainly by operational risk teams to ensure governance, and then we have the internal audit teams in 3rd line of defense, presenting their findings to the Board, there is also the 4th line that is the regulatory bodies like SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission), FINRA (Financial Industry Regulatory Authority) with their adhoc audits to ensure compliance with the overarching regulations in the financial space.
Apart from the assessments, there is business as usual work on the security side with security architecture reviews for any new application or system being designed, there are vulnerability management and incident management programs that generate portfolio of work on the risk matters. Information security managers can streamline all of these findings, controls gaps, potential risk items through governance forums. They actively work with risk owners and accountable executives to facilitate these discussions. Their opinion matters the most in consulting capacity during these risk discussions. These governance forums act as Steering committees which facilitate Risk response from Senior management keeping in mind the organization context of Risk appetite and Risk tolerance [9,10].
There is a very simplistic structure of governance forums in financial services, critical/high risks are guided through all governance forums across first and second line of defense and make it to the Senior leadership, while moderates and lows make it through first line and a few forums in second line for visibility and insight of the operational risk management teams. Third line of defense also called as the Internal Audit teams don’t organize governance forums since they are an independent assessing body within the firm.
Information Security Managers also leverage various dashboards for risk reporting purposes and actively contribute to the continuous monitoring exercises.
Role of information Security managers extends to the entirety of financial services from big banks to startups to investment firms, information security managers can work with CISO and teams in improving the risk posture. They can interact with the business teams, legal counterparts and security architects. Information Security and risk managers can work well with regulators over the course of Audits to understand context. They are consulting and advisory capacity which helps stakeholders and systems owners to get perspective and insight into the holistic risk posture. These positions work well in technology firms too for Risk reporting purposes and having technical conversations with security architects on control implementations.
Role of an Information Security manager is very crucial in not just financial firms but in any line of business, since, they have the required expertise to tackle compliance situations but at the same the technical knowledge to work with security subject matter experts and system owners, thus bridging the gap between various stakeholders. As the threat landscape continues to evolve and there is more budget spend in areas of security, it’s important to have resources at every level and with varied skill sets to deliver on that vision of secure operating environment. Information security managers can step in reduce the compliance and interface with other security teams to help system owners understand a holistic risk picture so that they don’t end up in a complex world of building security controls, right thing to do is balancing business objectives with security to deliver on leadership’s vision [11,12].
