Author(s): <p>Ghirardi Graciela Rosa*, Carmelo Caballero and Alfonso Heras</p>
Introduction: Penile cancer is not common in developed countries, although it is common in some Latin American countries. It is related to cervical cancer, it has two independent cancer pathways, according to its link or not, with HPV. Therefore, it is relevant to promote vaccination in young men. Given the clinical / oncological management has new treatment proposals based on immunotherapy (IT), which favors preservation of the organ, the pathology reports must be increasingly strict in terms of classification, Immunohistochemical (IHC) markers, and therapeutic strategies.
Objectives: To assess the perspective on the use of established HPV and IT IHC markers to establish the relevance of their use; determine the specificity and sensitivity of the markers through IHC.
Materials and methods: 27 samples of penile cancer were evaluated, from patients from Paraguay, who underwent HPV IHC and IT to establish their relevance with 16 markers.
Results: The IHQ markers: MCM2, MDM2 and HSP-27 were very significant in the cancer / HPV ratio; PDL-1, CD4, CD8 and B7H3 were relevant for IT. According to our results, we recommend the HSP-27 and the B7H3 as markers.
Conclusion: The management of samples and histopathological typing should be performed by experienced pathologists in the pathogenesis, classification and therapeutic of penile cancer. It remains to unveil its real practical use, the degree of participation of agents and or cofactors, the local and systemic immune response, new drugs and vaccine efficacy. We suggest expanding the number of cases to confirm these results.
Penile cancer is rare, occurs in older adults and more those with phimosis, HPV, HIV, smokers and uncircumcised. The usual treatment is surgical treatment (excision), laser ablation, local radiation and partial or total penectomy. The prognostic and therapeutic depends on the staging TNM [1]. Currently, immunotherapy is used to inhibit checkpoints Immune controls such as PD1 and its PD-L1 ligand, which are important therapeutic "targets" in penile cancer [1]. T lymphocytes are powerful immune cells that can destroy tumors, but cancers have developed tricks to avoid death. The cancers are persistent and progress regardless of the presence of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL). TILs are considered predominantly "depleted" due to chronic antigen exposure, but recent studies have revealed that T cells in tumors exist in a continuum of epigenetic, transcriptional and metabolic states [2]. One paradox of tumor immunology is that the specific TIL tumor antigen are dysfunctional in situ and however may mediate regression of large tumors after blocking metastatic point immune control or adoptive transfer of cells [1]. However, persistence and progression would be influenced by the immune status of patients, and that those who have HIV with low immune competitiveness [3].
Determine the expression of immunotherapy markers by Immunohistochemistry (IHC) in penile cancer.
They were evaluated 27 FFPE tissues of penile cancer from patients from Argentina and Paraguay, which were tested by IHC with HPV and Immunotherapy markers (Table 1 and 2)
Table 1: HPV IHC Antibodies (Bio SB, Santa Barbara, CA, USA)
| Antibodies | Clone |
| p16 | 16P04, JC02 |
| Ki-67 | EP5 |
| MCM2 | RBT-MCM2 |
| Topoisomerase IIa | RBT-Topo2a |
| HSP-27 | G3.1 |
Table 2: Immunotherapy IHC Antibodies (Bio SB)
| Antibodies | Clone |
| PD-1 | NAT-105 |
| PD-L1 | RBT-PDL1 |
| LAG-3 | EP294 |
| B7H3-CD276 | RBT-BTH3 |
| CTLA-4 | RBT-CTLA4 |
| OX-40 / CD134 | BSB-90 |
| FOXP3 | EP340 |
| CD8 | C8 / 144B |
| CD4 | RBT-CD4 |
| GATA3 | EP368 |
| T-bet | EP263 |
| MDM2 | BSB-64 |
• Pipettes and pipette tips: variable ranges
• Pressure cooker
• Ink detection system and preparation support
• TintoDetector Cap Gap System (Bio SB, Cat BSB 7000)
IHC Reagents / Ancillaries (Bio SB):
• Xylenes
• 30% -100% EtOH
• Distilled water
• ImmunoDNA Washer 20X (wash buffer solution)
• ImmunoDNA Citrate 20X (HIER solution)
• M/R PolyDetector Plus HRP / DAB Detection System
• Antibodies (Tables 1 and 2)
Our descriptive study was carried out by analyzing 27 FFPE tissues from patients with penile cancer from Argentina and Paraguay. Table 3 and Figure 3, display the most notable findings: POSITIVE patients for HPV had 93% positivity for B7-H3/ CD276 and only 7% positives in Non-HPV Cases. In contrast, PDL-1 in Positive HPV patients had only 47% positivity and CD4 73% positivity, plus MDM2 and HSP-27 were 100% positive on HPV positive patients. Figures 1 and 2 show photomicrographs of our results.
Table 3: Percentage of IHC positivity rate of cases with and without HPV using Immunotherapy IHC markers
| HPV / STRONG | Non-HPV / SLIGHT | |
| PDL1 | 47% | 53% |
| CD4 | 73% | 27% |
| CD8 | 46% | 54% |
| B7-H3/ CD276 | 93% | 7% |
| Ki67 | 77% | 27% |
| MCM2 | 60% | 40% |
| MDM2 | 100% | 0% |
| HSP-27 | 100% | 0% |
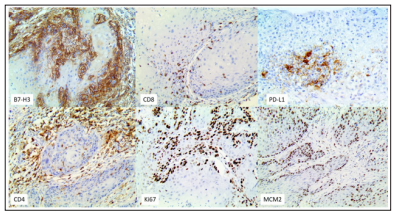
Figure 1: IHC of selected Immunotherapy markers on case 16- 9013
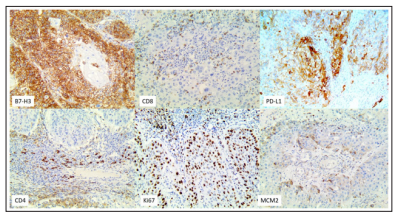
Figure 2: IHC of selected Immunotherapy markers on case 828
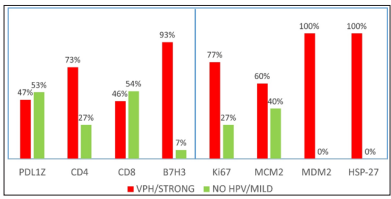
Figure 3: Percentages of cases with and without HPV using IHC immunotherapy markers. Values are represented in percentages. (n=27).
The use of PD-L1 and PD-1 have had great success in the treatment of different types of cancer, but only a fraction of the patient has obtained real benefits with this therapy, so it is urgent to seek more effective and specific alternatives. In this regard, Younghee Lee et al have published extensive information on this topic (4).They describe that they have treated mice with anti B7-H3, neutralizing the tumor growth of various types of cancers. The combined blockade of B7-H3 and PD-1 resulted in a synergistic effect on tumor growth inhibition (4). Everything suggests that B7-H3 could control the activation of neo- specific T- cells during related actions between APCs (antigen presenting cells) and T cells in secondary lymphoid organs (Figure 4).
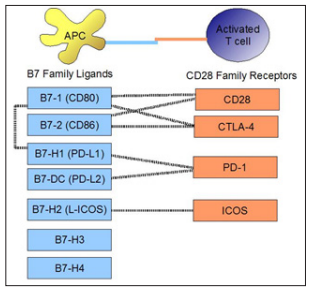
Figure 4: Diagram that shows the binding of costimulatory molecules on APC and T cells shows the ligands of the B7 family and their interactions with CD28 family receptors. Taken from: https://es.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:B7_family_ligands_and_ CD28_family_receptors.JPG
Recent studies showed an aberrant type of B7-H3 expressed in different types of cancer. However, the receiver for B7-H3 has not yet been identified.
It has been seen that PD-L1 and B7-H3 have similar expression patterns, but act at different sites (of tumor evasion) for carcinogenic progression and would, in theory, be synergistic in the anti-tumor effect. It would be important to detect the B7-H3 receptor to develop the path of the immune response to cancer.
Picarda et al published that B7-H3 would have a role important in the regulation of innate immunity, homeostasis and inflammation, although the elucidation of its "action" is complex and requires more understanding since its receptor still has not been discovered. Regarding the tumor microenvironment and immune evasion, it has been described that the overexpression of B7-H3 in tumor malignancy in humans and it has been observed that more than 60% and up to 93% of tumor tissues have aberrant expression in vast tumors by IHC, while that expression is limited in normal tissues [5].
Regarding the tumor evasion sites of PD-L1 and B7-H3, they are expressed in myeloid cells and tumor cells. Recent findings show that PD-L1 in tumor cells is sufficient to confirm invasion in immunogenic tumors which inhibits the cytotoxicity of CD8 cells.
The immunological role of PD-L1 and B7-H3 is therefore not redundant, in antitumor immunity. In terms of antitumor activity, both anti PD-1 antibodies and anti PD-L1 (approved by the FDA) have demonstrated effectiveness in multiple tumors [5].
The scientific community is beginning to explore the therapeutic role of B7-H3 in various courses of action that includes the synergism of target therapies and could be the bridge to effective therapies in human cancers.
According to Young-hee and collaborators in 2017, the inhibition of B7-H3 immune control points, limits tumor growth through activation of toxic cytocytes, with interaction between a tumor and the immune system. Favorable responses with Immunotherapy anti CTLA4, PD-1 and PD-L1 have been observed, although only a small number of patients responded to these therapies. In addition, they indicate the need to explore additional co - inhibitory molecules, such as B7-H3 member of the B7 super family, where the inhibition of T-cell activation and autoimmunity has been observed [4].
In a Research 2019,a study on cancer of lung of small cells analyzed the expression and clinical significance of PD-L1, B7- H3, B7-H4 and TILs, checking activity limited to the use of monotherapy with PD- 1 / CTLA4 to block control immune points, a situation that makes people think about exaggerated expectations in properties and results regarding these markers [6].
The same authors measured objectively 3 members different from the B7 family and TILs and found low levels of PD-L1, B7-H4 and TILs, but a prominent expression of B7-H3, like us. Which could mediate immune evasion in these tumors and, perhaps, a new therapeutic opportunity [6].
Varki et al, analyzed squamous cell carcinoma in skin and the expression of markers PD-L1, B7-H3 and PD-1 in relation to immunosuppression in 66 cases and their immune status. They found that the expression of PD-L1 was 26%, B7-H3 85%, and the expression of PD-1 and CD8 TILs was 80%. Their conclusion is that results vary based on immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients both and that B7-H3 would be useful in immunocompetent and transplant patients. In addition, they published that the expression of B7-H3 was very high in immunocompetent patients and very low in immunosuppressed patients with HIV [7], which we did not research.
In the context related to vaccines, and HPV- associated malignancies, WHO recommends vaccination not only for women but also for men, in national vaccination programs (Figure 5). In Europe, the European Center for Disease Control and Prevention (ECDC), the United States, Australia and Canada, recommend inclusion of this vaccine to the male population as part of vaccination programs [2].

Figure 5: Efficacy of the tetravalent vaccine in different clinical manifestations of HPV in men. Adapted from: Crosignani P. et al [8].
Sample management and histopathological typing should be performed by experienced pathologists according to recent advances in their pathogenesis, classification and therapeutic strategies of penile cancer. It remains to reveal its real practical use, as well as the degree of participation of certain agents or cofactors, in addition to the local and systemic immune response and the way in which new drugs could act to improve and/or control the infection. We consider appropriate to continue contributing to the knowledge about B7-H3, as it could serve as a new target for cancer immunotherapy.
Our work has limitations such as not knowing the tumor status and immune status of the cases, clinical and epidemiological data.
This author has no conflict of interest in analysis and results because she does not have funding or work for a multinational Laboratory. Nor does it have financing or contribution in the data obtained or in evaluation or technical support.
