Author(s): Muthahharah Mutiara Andi*, Rasdiyanah, Fitriani Aidah, Sutria Eny and Titi Mildawati
Background: Hypertension is the main cause of premature death worldwide. Hypertension has become a global, regional, national, and local public health problem. Hypertension requires proper self-management and health literacy in handling it.
Methods: Correlational anality descriptive research design using a cross-sectional study approach. Sampling technique using non-probability sampling with purposive sampling technique. The sample obtained is 128 people. Data collection used the HELIA Questionnaire (Health Literacy Instrument for Adults) and the HBP-SCP Questionnaire (High Blood Pressure-Self Care Profile).
Results: The results showed that the majority of respondents had low health literacy with a percentage of 56.3% and the majority had poor hypertension management behavior with a percentage of 54.7%. The results of the bivariate test using the Chi-Square test with a significance value of 0.006 <0.05, so that the better a person's health literacy, the better his hypertension self-management behavior.
Conclusions: The conclusion of this study is there is a significant relationship between health literacy and hypertension management behavior in the community in the Pacellekang Health Center work area, Gowa Regency.
Hypertension has become a world, national, regional, and local public health problem. Hypertension is currently a big challenge in Indonesia due to conditions that are often found in primary health services. The World Health Organization (2023) estimates that 1.28 billion adults aged 30-79 years worldwide suffer from hypertension.
According to the South Sulawesi Provincial Health in 2018 there were 229,720 cases of hypertension that occurred, then increased in 2020 by 381.13 cases, one of the districts in South Sulawesi with 33,721 people with hypertension, namely Gowa Regency [1]. One of the areas in Gowa Regency with a fairly high prevalence of hypertension is the working area of Public Health Care Pacellekang.
Management of a chronic disease requires self-care-management,adherence to recommended medications, and self-modification and lifestyle. This is related to the level of health literacy. Health literacy or health literacy has an important role in health promotion. This is because health literacy plays a role in community empowerment.
Health literacy can be used to determine the motivation, level of knowledge, and ability of the community to access, assess, understand, apply health information by making considerations and decision-making in daily life related to health.
Based on the description above, researchers are interested in conducting research related to the relationship between health literacy and self-management of hypertension groups in the working area of the Public Health Center Paclelekang, Gowa Regency.
This research was conducted in the working area of the Public Health Care Pacellekang, Gowa Regency, in June-July 2023. This research design includes quantitative research, namely descriptive correlational analytics with a cross sectional study approach. The sampling technique used in this study is purposive sampling technique, where samples are taken Based on the Slovin formula, a sample of 128 people was obtained. The instruments used in this study were the HBP-SCP (High Blood Pressure-Self Care Profile) questionnaire and the HELIA (Health Litercay Instrument for Adults) questionnaire.
Table 1: Frequency Distribution of Respondent Characteristics Based on Gender, Age, Recent Education, Occupation, and Health Resources
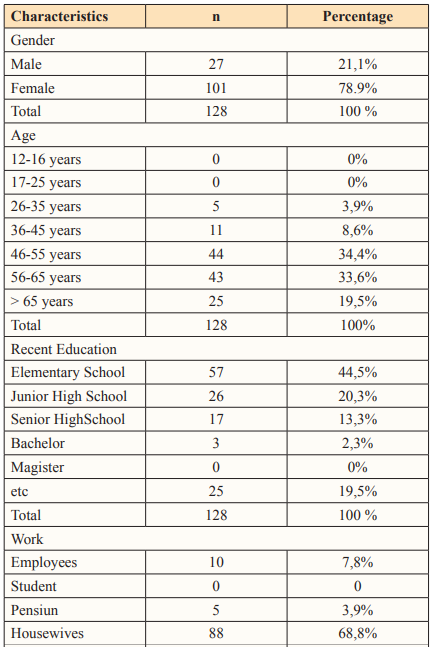
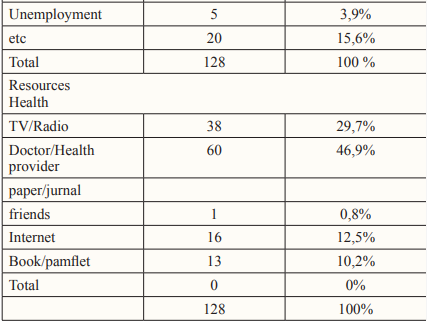
Source: Primary Data, 2023
The characteristic description of hypertensive clients is the majority aged 45-55 years with a percentage of 34.4%, female gender as many as 101 respondents (78.9%). Community respondents had the last level of elementary education as many as 57 respondents (44.5%). The most jobs were housewives as many as 88 respondents (68.8%), and the most sources of information used were through doctors/health services at 46.9%.
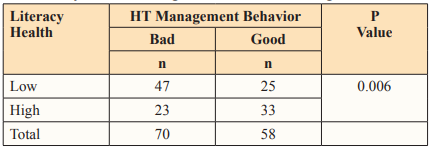
Table 2: Results of Data Analysis of the Relationship between Health Literacy and Hypertension Management Behavior in the Community in the working area of the Pacellekang Health Center
In table 2, it shows an overview of the level of health literacy and hypertension managemeynt behavior in hypertensive clients in the Public Health Center Pacellekang Work Area. Most respondents had a low health literacy rate of 72 people (56.3%) and those with a high health literacy rate of 56 people (43.8%). Meanwhile, most respondents had a poor level of management behavior of 70 people (54.7%) and those with good management behavior of 58 people (45.3%). Based on the results of bivariate analysis using the Chi Square alternative test, p values were obtained from 0.006 < 0.05. This shows that there is a significant relationship between health literacy and hypertension management behavior in the community in the working area of the Pacellekang Health Center.
Based on univariate analysis, respondents' characteristics based on sex are dominated by the female group. One of the factors causing women to have a tendency to have a higher incidence of hypertension than men is that women experience menopause [2]. The characteristics of respondents in terms of age found that the average respondent was at the age of 46-55 years. It is known that with age, the prevalence of hypertension increases. This is due to physiological features in the body, such as the thickening of artery walls due to plaque buildup in the endothelial layer so that blood vessels experience narrowing and stiffness, resulting in changes in blood pressure to be higher.
The characteristics of respondents based on the last level of education are most elementary schools. This is in accordance with the statement that the level of education related to health information obtained affects a person's ability to receive information and process it into good behavior so that it has an impact on his health status.
Characteristics of respondents based on work, the results of this study show that respondents who experience hypertension are respondents who are IRT. This is supported by research conducted by Elsi (2022) which shows that good hypertension prevention behavior based on the work of working respondents is higher than that of non-working respondents [3]. Based on the RISKESDAS Indonesia-Year 2013 report, the highest prevalence of hypertension is found in non-working groups. The risk of hypertension in people who do not work can be greater because of the lack of regular physical activity. The characteristics of respondents based on health information sources show that respondents obtain the most health information through doctors/services. One Research found that there is a significant relationship between information sources and the application of clean and healthy living behaviors (PHBS) in the family.
Based on these results, researchers argue that the health literacy of hypertensive clients in the work area of the Pacellekang Health Center still shows low health literacy. This is because the level of education of the community is also still relatively low, which affects the level of health literacy.
Based on univariate results using frequency distribution, it was found that the average hypertension management behavior in respondents in the work area of the Pacellekang Health Center was in the poor category. This is due to the lack of knowledge related to hypertension control, as well as less exposure to health information in carrying out hypertension self-management.
Based on the results of bivariate analysis using the Chi-Square alternative test, p values were obtained from 0.006<0.05. This shows that there is a significant relationship between health literacy and hypertension management behavior in the community in the working area of the Pacellekang Health Center.
The results of this study are in line with research conducted by Roiefah et al. which states that there is a significant relationship between the level of health literacy and NCD prevention behavior in adolescents. The low percentage of understanding is due to the low knowledge of respondents, and the difficulty of respondents in understanding information on non-communicable disease prevention behaviors. This happens because respondents' habits to access information are still lacking and sources of information are limited.
According to researchers, health literacy in hypertension clients showed low results with a percentage of 56.3%, thus affecting hypertension management behavior, which on average respondents were not good at managing hypertension.
There are several factors that affect self-management in people with hypertension, including knowledge, education level, social support, self-confidence, and long-suffering from hypertension. Patients who have a high level of knowledge will increase self- confidence and grow patient awareness regarding the importance of treatment. Thus, understanding of a disease must be done holistically from all aspects, such as aspects of diagnosis, risk factors, prevention efforts, and also complications. If people with hypertension do self-management effectively, it will certainly be useful to generate satisfaction in their health, reduce the cost of treatment, generate confidence and independence of patients, and improve the quality of life of patients.
Health literacy is related to the disease experienced by a person. In addition, confidence in health also acts as a guide to the coping that will be applied by individuals when overcoming their health problems.
There is a relationship between health literacy and hypertension management behavior in Pacellekang Village showing significance values (p value 0.006 < 0.05). Therefore, community health care can increase posyandu and prolanis activities as well as carry out health promotion as a form of increasing interest in hypertension control for the community. In addition, hopefully, community health care can also add sources of health information such as pamphlets or distribution/brochures in their work area, so that people can be exposed to health information, not only orally but also in writing [4-11].
The study team strictly followed ethical standards in research, ethics approval documents are available by No. C.012/KEPK/ FKIK/II/2023 ethical committee UIN Alauddin Makassar; we ask for approval before becoming a participant, all individual information was strictly kept confidential and not reported in the paper.
