Author(s): Zixin Qian*, Chao Feng, Yuhang Chen, Yuanjie Lin, Ziwei Liang, Hailei Qian, Jingxian Zhou, Jinjing Ma, Yue Jin, Dasheng Lu, Guoquan Wang, Ping Xiao and Zhijun Zhou
As regulations ban legacy PFASs, many emerging PFASs are being developed, leading to their release into the aquatic environment and drinking water. However, researches on these emerging PFASs in drinking water are limited, and current standards only cover a few legacy PFASs, leaving many emerging PFASs unregulated and their toxicity unknown. Therefore, a machine learning-based suspect screening method was employed to comprehensively identify and quantify both legacy and novel PFAS in drinking water from the Yangtze River Delta, and their potential sources of contamination were determined through pollutant profile analysis. Then, the identified PFASs were prioritized by integrating the PBT (persistence, bioaccumulation, and toxicity) properties of PFASs with environmental exposure data. A total of 30 PFASs were identified, including 16 legacy and 14 novel PFASs, categorized into 11 classes. The pollutant profile analysis suggested that PFASs in the Yangtze River Delta’s drinking water are more likely to originate from pollution in the upper and middle reaches of the Yangtze River rather than from local industrial emissions. In the prioritization and risk assessment process, ten high-concern PFASs had Risk Index (RIs) higher than those of ref-PFOA and ref-PFOS, including eight legacy PFASs and two novel PFASs. The drinking water of Yangtze River Delta originates from the surface water of the lower Yangtze River, which accumulates pollutants from its upper and middle reaches, affecting the health of over 20 million people. Our findings indicated the presence of emerging PFASs in the region’s drinking water and demonstrated conceptual models for integrating chemical information from suspect screening with toxicity prediction and risk assessment. Although the current levels of emerging PFASs are relatively low, legacy PFASs still dominate. Further research is needed to identify, monitor, and assess the health and environmental risks of emerging PFASs.
Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) are a class of anthropogenic synthetic compounds with high-energy covalent bonds, which are widely use in a variety of industrial and consumer applications due to their hydrophobicity, lipophobicity, high thermal and chemical stability [1]. Due to their widely application and exceptional physicochemical properties, PFAS are almost ubiquitous in the environment [2]. Numerous epidemiological and toxicological studies have demonstrated that exposure to PFAS can cause a series of adverse effects on human health, including developmental and reproductive toxicity, neurotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, genotoxicity, immunotoxicity, endocrine toxicity, and carcinogenicity [3-9]. The persistence and toxicity of PFAS have raised global concern about their potential environmental and health risks. In order to control the contamination and health hazards caused by PFAS, many countries and international organizations are implementing regulations to limit the manufacturing and utilization of some legacy PFASs, which has led to a growing number of manufacturers turning to the production of new alternatives of PFASs [10]. However, adequately safety tests are lacking for these novel PFASs, and companies refuse to disclose their components citing trade secrets, making it difficult for regulatory agencies and the public to comprehensively assess their safety and long-term impacts [11]. Many of these novel PFASs are discharged into the environment and have been detected in both environmental and biological samples [10,12-15]. Previous studies have indicated that the toxicity of certain novel PFASs may be comparable to or even exceed that of legacy PFASs [16-19]. Many novel PFASs shown higher affinity in molecular docking experiments with PPARα and ERα receptors than legacy PFASs [20].
Drinking water is one of the main pathways of human exposure to PFASs [21]. To safeguard public health, numerous countries and organizations have implemented standards for PFAS limits in drinking water. In 2024, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) established Maximum Contaminant Level (MCL) standards for six PFASs in drinking water. The specific standards are as follows: PFOA at 4 ng/L, PFOS at 4 ng/L, PFHxS at 10 ng/L, PFNA at 10 ng/L, and HFPO-DA (GenX) at 10 ng/L. Additionally, the Hazard Index MCLs for mixtures containing two or more of the substances PFHxS, PFNA, HFPO-DA, and PFBS should be less than 1[22]. Chinese sanitary standards for drinking water stipulated that the concentrations of PFOA and PFOS should not exceed 80 ng/L and 40 ng/L, respectively. The current standards are primarily aimed at legacy PFASs and a small amount of novel PFAS. However, a significant portion of novel PFASs are not covered by existing standards of drinking water, and their toxicity remains largely unknown. Thus, comprehensively identifying and evaluating the risks of legacy and novel PFASs in drinking water is of utmost importance.
Many studies have demonstrated that target PFASs constitute only a minor portion of the total organic fluorine (TOF) present in living organisms and the environment. In fact, a significant portion of extractable organic fluorine (EOF) is attributed to unidentified PFAS [23]. EOF mass balance analysis revealed that target PFAS account for less than 36% of the EOF in drinking water from Shanghai [24]. This indicated the presence of a significant amount of unidentified organic fluorine compounds in the drinking water, underscoring the importance of identifying and studying these unknown pollutants. Currently, the majority of studies on PFAS in drinking water primarily focused on the routinely monitored targeted PFAS. However, the utilization of high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) had enabled both suspect and non-targeted screening methods to identify unknown PFAS compounds within complex environmental samples [11]. Only a few researches had conducted suspect and non-targeted screening of PFASs in drinking water, but none of these studies had considered the toxicity and risk assessment of these emerging PFASs [24-27]. Linking the chemical information obtained from non-targeted screening to the toxicity of compounds is vital for risk assessment. This linkage is essential for identifying and evaluating potentially harmful substances that may not be regulated, thereby enhancing our ability to protect public health and the environment [28]. The Toxicological Prioritization Index (Toxpi) framework was designed to integrate multiple sources of information about exposure, compound properties, health and environmental risk, enabling a comprehensive prioritization of chemicals based on their hazards to facilitate informed decision-making [29-31]. It was frequently utilized for risk assessment of multiple emerging pollutants in food, biological samples and environmental media [12,32-35].
Yangtze River Delta is located in downstream of the Yangtze River, near its estuary. The local drinking water mainly relies on the surface water of the Yangtze River, which gather various pollutants from the upper and middle reaches of the Yangtze River and are vulnerable to further contamination [36]. With the rapid urbanization and industrial development along the region of Yangtze River, large amounts of industrial wastewater, domestic sewage, and agricultural runoff flow into the Yangtze River and its tributaries, resulting in a gradual deterioration of water quality [37]. Therefore, the safety of drinking water in Yangtze River Delta has become particularly crucial. As a major economic center in China, the drinking water safety in Yangtze River Delta directly affects the health of more than 20 million residents [24]. Ensuring the purity and safety of drinking water is not only an important measure to protect public health but also a key to maintaining regional economic stability and development.
In this study, a total of 49 drinking water samples were collected from Yangtze River Delta. The aims of the study were to (1) comprehensively investigate the occurrence and concentrations of legacy and novel PFASs in drinking water samples through the combination of target and suspect analyses; (2) identify the potential sources of PFAS in drinking water of Yangtze River Delta by analyzing the contamination profiles of PFAS in drinking water, surface water adjacent to potential industrial emission sources in the local area, the Taihu Basin, and the Yangtze River; (3) prioritize and risk assessment of identified PFASs according to their potential hazard effects and environmental exposure. The findings of our study would provide valuable insights into the prevalence of PFASs in drinking water from Yangtze River Delta and the associated exposure risks among the general public.
Authentic standards of 68 target PFASs along with their 13 corresponding internal standards were purchased from Wellington Laboratories Inc. (Guelph, Ontario, Canada) for target analysis, and detailed information of these PFASs is provided in the Supporting In-formation (Table S1). The mixed standard solution and the mixed internal standard solution were prepared separately in methanol at 100 μg/L and stored at −20 ?C. The ultrapure water was generated by a Milli Q system (18.2 Ω, TOC < 5 ppm, Merck, New South Wales, Australia) and HPLC grade methanol and acetonitrile were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (New South Wales, Australia). Besides, all the other reagents (e.g. ammonium hydroxide, ammonium acetate) were purchased with HPLC grade from reliable suppliers.
Samples were collected in August 2023. A total of 49 water samples were obtained from Yangtze River Delta, including 5 source water samples, 24 treated water samples, and 20 tap water samples. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) bottles (1L) and their caps were pre-rinsed using methanol (MeOH) and HPLC-grade water, then dried before use. Tap water samples were collected using the following procedure: operators wore laboratory nitrile gloves during sample collection, the tap water was allowed to flow for approximately 3 minutes, and the HDPE bottles were rinsed three times with tap water from the site before being filled. The collected water samples were stored at 4°C and extracted within 48 hours using the routine solid-phase extraction (SPE) method.
Before extraction, 100ml water samples were added 0.925g ammonium acetate (adjust PH to 6.8-7) and spiked with the internal standard solutions (20 μL of 100 μg/L each) before SPE. The extraction of water samples was performed by Oasis WAX Cartridges (150 mg, 6 mL, Waters). Briefly, the cartridges were preconditioned by 5 ml of 0.1%NH4OH in methanol, 5 mL of methanol and 10 mL of Milli-Q water in sequence, then the water samples were passed through the cartridges at a flow rate of approximately 5-10 mL/min. After sample loading, the cartridges were rinsed by 5mL 25mmol/L ammonium acetate solution and 10mL ultra-pure water and then dried under vacuum for about 15min. The WAX cartridges were hereafter eluted by 2mL of methanol and 4 mL of 0.1%NH4OH in methanol in succession. The eluents were nearly dried under a gentle stream of nitrogen and re-dissolved with 200ul 60% methanol aqueous solution. After vortex mixing, the sample were centrifuged at a rotating speed of 16000 RCF for 3min. Then, the supernatants were collected into the sample bottle for analysis.
Target and suspect screening of the water samples was performed using an Agilent 1290 Infinity II LC system coupled with an Orbitrap ExplorisTM 240 Mass Spectrometer (Thermo Scientific, San Jose, CA, USA) with electrospray ionization (ESI)source. Samples (5 μL) were injected onto an Agilent Infinity Lab Poroshell 120 EC-C18 analytical column (3.0 × 150 mm × 2.7 μm) with the column oven temperature set at 40 °C. Data acquisition was operated in negative ionization mode, utilizing both full scan (150−1500 Da) and data- dependent MS2 (ddMS2) scans to ensure comprehensive feature collection. The detailed parameters of chromatography and mass spectrometry parameters can be found in the Supporting Information (Text S1).
The suspect screening process (Figure 1) was conducted in accordance with our previous research [13]. An in-house library was established using 68 reference standards. This library was utilized for target screening and the development of a machine learning-based retention time (RT) prediction model. We collected four lists for suspect screening, including PFASSTRUCT v5 (14,735 PFASs, 785 cationic PFASs, as of August 2022) and PFASMASTER (12,043 PFASs, 817 cationic PFASs, as of August 2021) from the US EPA CompTox Chemistry Dashboard, FluoroMatch v3.3 (7,206 PFASs, 493 cationic PFASs, accessed in September 2023), and “Suspect List of Possible PFAS” v1.7 (PFAS-Nist, 4,967 PFASs, 539 cationic PFASs, DOI: 10.18434/ mds2-2387, January 2023). These lists were compiled to build a comprehensive database, which was then screened using Compound Discoverer 3.3 (Thermo Scientific, USA). Key criteria for feature filtering in raw data included precise m/z values (<5 ppm), intensity >5 times the intensity in the extraction blank, IPs (fit threshold >70%, allowable intensity deviation <30%, and mass deviation <5 ppm), predicted retention time (<1.5 min), and identification of at least one characteristic fragment ion (<10 ppm). For structural confirmation, the formula-assigned features from suspect screening were further annotated by manual interpreting their fragment ions or comparing their MS2 spectra with literature. Positive identification required at least one characteristic fragment could be explained. The proposed structures were assigned three confidence levels (CL) based on criteria established in Charbonnet et al.’s study [38].

Figure 1: (a)Workflow for Target, Suspect Screening of PFAS and Prioritization and (b) Proposed Structures of PFAS Identified by the Target, Suspect Screening
In our study, a neural network model was developed to semi-quantify 10 PFASs without authentic standards by predicting their response factors (RFs), which are the slopes of the linear regression lines in the calibration curves. The RF prediction model was constructed using 68 reference standards. A molecular descriptor set containing 3,874 descriptors was generated from the 2D structures (canonical SMILES from PubChem) of these standards using alvaDesc v2.0. The RFs and molecular descriptor set of all 68 standards were randomly divided into training and test sets in an 8:2 ratio for model training. The neural network algorithm, implemented in the Optuna mode (mljar-supervised v1.0, Python package), was employed to automatically tune the machine learning parameters. Over 5,000 models were generated with various parameters, and the model with the best RMSE was selected as the optimized model. Using this optimized model, RFs for 10 PFASs without authentic standards were then predicted.
A 100mL volume of ultrapure water, spiked with the same internal standard solutions as the water samples, was used as a procedural blank to evaluate potential contamination during the extraction and analysis processes for each batch. The method LOD and LOQ values for 47 PFASs were detailed in the Supporting Information (Table S2). The calibration curves for each target compound exhibited high correlation coefficients (r² > 0.99) (Table S2). Additionally, during the instrumental analysis, a standard mixture solution and methanol were sequentially injected following every six samples to act as calibration standards and blanks for data acquisition.
Results from animal experiments, in vitro tests, and epidemiological studies suggested that some PFASs can disrupt the endocrine system, interfering with the secretion of sex hormones and thyroid hormones, and impacting normal reproductive ability, the nervous system, and immune function [39-43]. Receptor mediation is the primary mechanism by which compounds exert endocrine- disrupting activity [39]. Therefore, to assess the endocrine- disrupting effects of PFASs, six human hormone receptors (thyroid hormone receptors alpha (TRα, PDB ID: 3jzb) and beta (TRβ, PDB ID: 3gws), estrogen receptors alpha (ERα, PDB ID: 1ere) and beta (ERβ, PDB ID: 5toa), androgen receptor (AR, PDB ID: 3l3x) and peroxisome proliferators-activated receptors(PPARα, PDB ID:3vi8)) were selected for the receptor-ligand docking study. Molecular docking simulations were conducted using Biovia Discovery Studio 2021 software. The specific processes were referred to in our previous research [13]. The Libdock scores were utilized to assess the binding affinity between the compound and the active site of the receptor, with higher scores indicating stronger affinity.
To prioritize the identified PFASs and pinpoint those of high concern,

Targeted and suspect analyses were performed using Trace Finder 5.0 software (Thermo Fisher Scientific, 2021, Waltham, MA, USA) and Compound Discoverer 3.3 software (Thermo Fisher Scientific, 2021, Waltham, MA, USA), respectively. The principal component analysis was conducted using SIMCA 17 software (Sartorius Stedim Data Analytics 2021, Umeå, Sweden).
Concentrations and Compositions of PFASs in Drinking Water After preprocessing the raw data, we generated 414,397 peaks. Using suspect screening with blank subtraction and a retention time versus m/z filter, we identified 475 possible positive hits. Following the removal of duplicates and poorly shaped peaks, 88 peaks were selected for MS/MS spectra annotation. Through further structural elucidation based on diagnostic fragments, we ultimately identified 30 PFAS in the drinking water from Shanghai. Among these 30 PFAS, 12 legacy PFASs and 7 novel PFASs were confirmed using authentic standards.
These 30 PFASs could be divided into 11 categories:(1)perfluoro carboxylic acid (PFCAs), (2)perfluoro sulfonic acid (PFSAs), (3)perfluoroalkyl dioic acids (PFdiOAs), (4)hydrogenated PFCAs (H-PFCAs), (5)hydrogenated PFSAs (H-PFSAs), (6) polyfluoroalkyl ether carboxylic acid(PFECAs), (7)fluorotelomer sulfonic acids (FTSAs), (8)chlorinated polyfluoroalkyl ether sulfonates (Cl-PFESAs), (9)hydrogenated polyfluoroalkyl ether sulfonates (H-PFESAs), (10)perfluoroalkyl sulfonamide(PFSMs), (11) HNTf2.
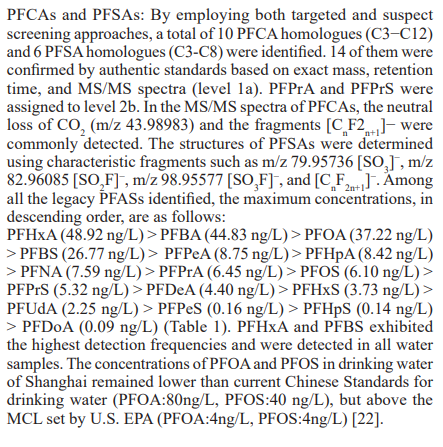

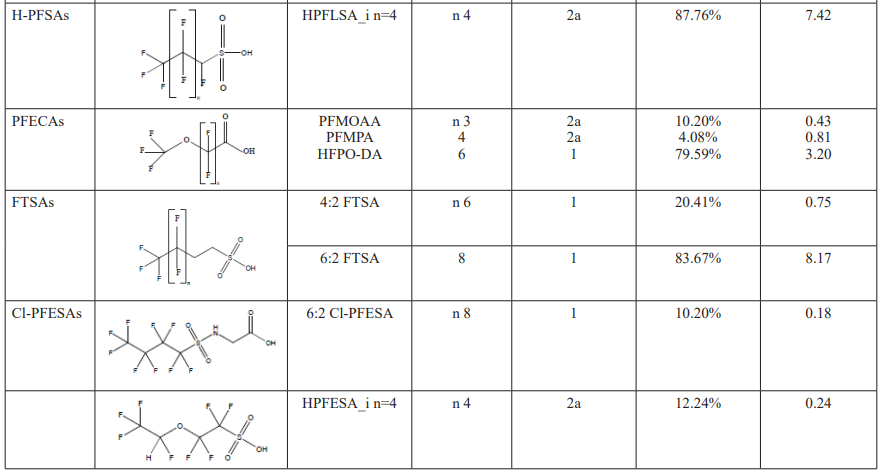
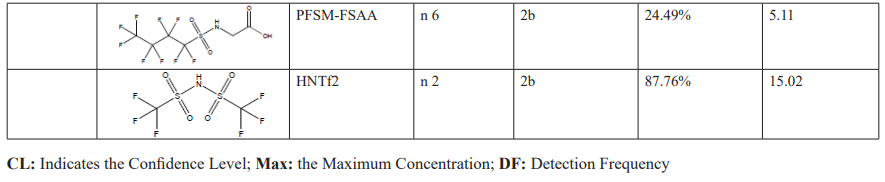
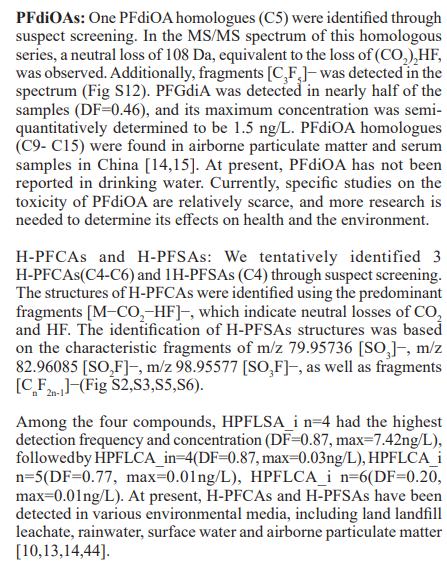
SW: source water; FW: factory water; TW: tap water samples; IA: international airport; Mi: industrial fluorochemical plant, Mp: metal plating plant; YR Yangtze River; HPR: Huangpu River;
Among all the 30 identified PFASs, two novel PFAS, 6:2FTSA and HNTf2, had been reported in landfill leachate of Shanghai [13]. Notably, the concentration of 6:2FTSA reached as high as 69.2 ng/ml, suggesting that municipal waste management might be another significant source of novel PFAS in drinking water from Yangtze River Delta.
To prioritize the identified PFASs and pinpoint those of high concern, we utilized a risk-based prioritization approach based on the research by Hu et al, with some modifications. Multiple hazard attributes were incorporated in our model, including persistence, bioaccumulation, ecotoxicological effects, human health effects, molecular docking scores, detection frequencies and concentrations [12]. By integrating these multi-dimensional data, our model provided a comprehensive assessment of the potential environmental and health risks associated with the compounds, helping to prioritize those requiring immediate attention and regulatory action. A total of based on PBT properties and molecular docking scores. The ToxPi scores of the 30 identified PFASs ranged from 0.09 to 0.85(Figure 3a), with PFDoA having the highest score, followed by PFUdA, PFDeA, and PFNA, all of which have higherscores than the traditional PFOA and PFOS. Generally, PFASs with longer carbon chains tend to have higher ToxPi scores. Among all the emerging PFASs, 6:2 Cl-PFESA has the highest ToxPi score (0.66), falling between the scores of PFOS (0.70) and PFOA (0.63). 6:2 Cl-PFESA, a proposed safe alternative for PFOS, may cause liver damage and induce lipid metabolism disorders in female mice through the action of PPAR-γ. Previous studies documented that the hepatotoxicity of PFOS and 6:2 Cl-PFESA appears to be higher than that of PFOA Previous studies documented that the hepatotoxicity of PFOS and 6:2 Cl-PFESA were higher than PFOA [52,53]. This indicated that we need to be mindful of the potential health and environmental hazards posed by these substitutes.
For persistence, the top 10 PFASs with the highest scores were PFDoA, 6:2 Cl-PFESA, PFUdA, PFOS, PFDeA, PFHpS, PFNA, 6:2 FTSA, PFHxS, PFOA (Table S7). Higher persistence scores indicated that these compounds were less biodegradable in the environment and might pose long-term risks to environmental and human health. There were a total of eight PFASs with persistence scores higher than PFOS and PFOA. Notably, the two substitutes for PFOS, 6:2 FTSA and 6:2 Cl-PFESA, had high persistence scores. Among them, 6:2 Cl-PFESA ranked second in persistence scores, even surpassing its predecessor, PFOS. For bioaccumulation, we selected logKow and BAF as the key attributes to evaluate the accumulation potential and associated risks of compounds within organisms. Among all the identified PFASs, the ones with the higher bioaccumulation potential were PFDoA, PFUdA, PFDeA, PFNA, and 6:2 Cl-PFESA. These compounds exhibited higher bioaccumulation than both PFOA and PFOS (Table S7). In terms of ecotoxicity, the PFASs with the higher toxicity scores were also PFDoA, PFUdA, PFDeA, PFNA, and 6:2 Cl-PFESA. We evaluated the human health effects of the compounds from five aspects: carcinogenicity, developmental toxicity, mutagenicity, skin sensitization, oral LD50 in rats and endocrine toxicity. The PFASs with the highest comprehensive score, in order, were PFHxS, PFPrS, PFHpS, HPFESA_i n=4, PFOS, 4:2 FTSA,
HPFLSA_i n=4, PFOA(Table S7). We found 11 PFASs with possible carcinogenicity, 2 PFASs with potential developmental toxicity and 5 PFASs with potential skin sensitization (Table S6). Based on the molecular docking scores with six receptors, the compounds with the highest total scores were PFNA, HPFLCA_i n=4, HFPO- DA, PFDeA, HPFESA_i n=4, PFOS, and PFOA.
The results indicated that some emerging PFASs exhibited higher affinity to receptors than PFOA and PFOS (Table S7). Additionally, we found that some long-chain PFASs, such as PFDoA, PFUdA, and PFDeA, had lower docking scores compared to PFNA, likely due to limitations imposed by their molecular size.
Based on the measured detection frequency and concentrations, we utilized toxpi scores to calculate the RIs, which represented a synthesized assessment for prioritizing chemicals based on potential health risks. The RIs ranged from 0-0.54 for 30 PFASs in water samples (Figure 3b). PFOA had the highest RI, followed by PFHxA, PFBS and PFBA. We found that some long- chain PFAS, such as PFDoA(Toxpi scores=0.85, DF=0.51,max=0.09 ng/L), PFUdA(Toxpi scores=0.77, DF=0.57,max=2.25 ng/L), exhibited higher ToxPi scores and posed significant environmental and health hazards, their RIs were not high when considering both detection frequencies and concentrations. Conversely, some short-chain PFAS, such as PFBA (Toxpi scores=0.17, DF=0.96, max=44.83ng/L) and PFBS (Toxpi scores=0.33, DF=1, max=26.77ng/L), despite had lower ToxPi scores, showed higher health risks due to their higher detection frequencies and concentrations (Table S7). To further identify the compounds of high concern, we selected the Maximum Contaminant Level (MCL) standard set by the EPA for PFOS and PFOA, which is 4 ng/L, as a reference dose for risk assessment of the identified PFASs. A total of 10 high-risk PFASs were identified through our method, including 8 legacy PFASs and 2 emerging PFASs. Of these, PFOA had the highest RI (RI=0.46), indicating it poses the highest risk. PFOA was closely followed by PFHxA, PFBS and PFBA, suggesting that we need to be aware of the health risks posed by these short-chain PFAS. HNTf2 and 6:2 FTSA were the two emerging PFASs with the high risk. In the future, more researches on their toxicity are necessary (Figure 3b).
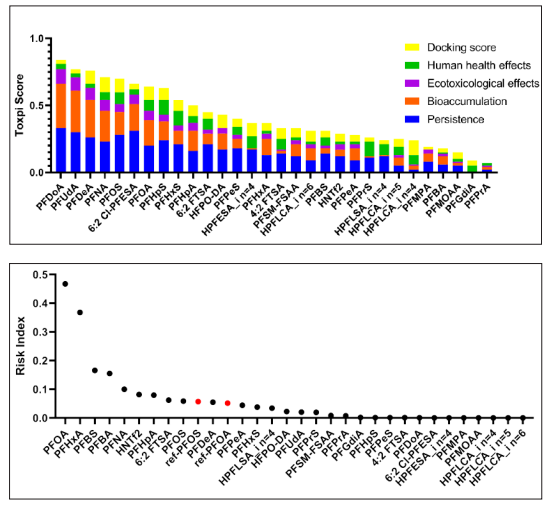
Figure 3: (a)ToxPi scores (b)risk index of 30 PFAS identified and quantified in drinking water from Yangtze River Delta
In this study, target and suspect screening analysis using UPLC- Orbitrap HRMS was implemented to identify the occurrence and concentrations of legacy PFASs and novel PFASs in drinking water from Yangtze River Delta. A total of 30 PFASs with high confidence levels (>3) were identified through both target and suspect screening, including 16 legacy PFASs and 14 novel PFASs. By utilizing the ToxPi framework and RIs, we evaluated and prioritized the risks of identified PFAS in drinking water by integrating various data. A total of ten high concerns PFASs were identified through our method. Currently, legacy PFASs were the largest contributors to PFASs in drinking water of Yangtze River Delta, accounting for up to 83% of ΣPFASs, while the concentrations of emerging PFAS were relatively low. However, with some countries and organizations implementing regulations to ban the use of certain legacy PFASs, many companies are developing new alternatives of PFASs and producing novel PFASs. This could result in increased concentrations of emerging PFAS in drinking water in the future. Therefore, more researches are essential to comprehensively identify and monitor various emerging PFAS in drinking water and evaluate their potential health and environmental hazards.
