Author(s): <p>Vedna Sharma* and Sourabh Jain</p>
The objective of this study was to develop an Inference System based on the Fuzzy Mamdani system for assessing the teaching skills of faculty members in academic or educational institutions. Nowadays, many academic institutions have adopted web-based methods to gather students' feedback on faculty members' teaching effectiveness. Evaluating faculty performance in teaching activities is crucial for establishing a more equitable academic environment. The primary goal of assessing faculty performance is to identify areas of strength and weakness in their professional development. This application of soft computing, specifically the Fuzzy Mamdani Inference System (FMIS), in evaluating faculty teaching performance can be valuable for organizational management in assessing faculty capabilities and their impact on student outcomes.
In academic institutions, the performance of teaching faculty is evaluated to enhance teaching quality and identify individual strengths and weaknesses. A teacher's quality encompasses various skills, personal attributes, and knowledge relevant to their specific subject area and effective assessment practices [1].
The evaluation of faculty performance within an educational organization involves coordination, planning, and assessment through multiple channels, including student feedback, peer assessment, and overall institutional examination results. When evaluating faculty teaching ability, it is important to differentiate between teacher quality and teaching quality, considering the benefits of research and student achievements [1].
To assess faculty teaching performance in an institution, it is crucial to plan and integrate review areas such as gathering student feedback and management assessment based on institutional or university results. The assessment criteria for faculty performance may differ across academic institutions, but the data collected is typically quantitative in nature. This data often lacks precision and certainty, making it suitable for analysis using soft computing techniques.
Conventional approaches to assessing faculty performance, primarily relying on student feedback, are not scalable for developing automated techniques. These traditional evaluation methods can be time-consuming and prone to calculation errors. In contrast, fuzzy-based systems are effective in handling uncertain datasets. Researchers have explored different techniques, such as Neuro Fuzzy Systems, to address this issue [2].
In this study, we employ a Fuzzy Mamdani Inference System (FMIS) for faculty evaluation based on student feedback. The FMIS is chosen due to its suitability for human inputs, easily comprehensible rule bases, and widespread acceptance. It assists in making decisions for performance appraisal and enables educational institutes and universities to exercise professional judgment in evaluating their faculty. In the Mamdani Inference System, the output of each rule is represented as a fuzzy set.
Odokuma et al. [3] have developed a system utilizing the Fuzzy Mamdani Inference System for assessing Academic System Requirements in Educational Organizations. The main objective of this study is to employ the Fuzzy Mamdani Inference System (FMIS) for evaluating Academic Standing and Continuation Requirements in Educational Institutes. The system aims to identify students who are at risk of failing out at an early stage. The research demonstrates that the model can effectively identify and provide guidance to students whose performance is below expectations, thus helping them avoid failure and dropout.
Ghosh et al. [4] have proposed a method for analyzing faculty teaching skills based on student feedback. This study introduces a ranking method that utilizes various fuzzy operators to compute the solutions of Fuzzy Relation Equations. The method deals with uncertainty in evaluating factors related to teacher performance. The authors propose a Fuzzy Expert System that employs fuzzy logic to evaluate faculty overall performance, particularly under conditions of "uncertain facts or data" in decision-making processes. The research aims to assist in writing annual performance reports, such as Annual Confidential Reports (ACR), for employees in organizations.
Yadav et al. [6] have utilized a fuzzy logic approach to evaluate the performance of teachers in academic institutes. This study presents a comprehensive method that encompasses various applications in educational systems, including not only the evaluation of students' academic performance but also the assessment of faculty members.
Khan, Abdur Rashid et al. [7] has proposed an Expert System with Fuzzy Logic for evaluating Teacher's Performance. This study demonstrates the use of fuzzy logic techniques to handle qualitative and undefined data in the decision-making process. The application of fuzzy logic in evaluating teachers' performance is an attempt to address these challenges. The authors developed a Proficient System that acquired domain-specific knowledge and obtained interesting results, providing a framework for researchers to explore solutions to various complexities in this field.
The faculty evaluation process involves systematically assessing Faculty Performance based on their professional contributions and role in achieving organizational objectives within a specific context. Intelligent fuzzy evaluation methods can aid in creating management rules and making optimized decisions by incorporating expert knowledge.
This research aims to develop an expert system utilizing fuzzy logic techniques for evaluating teachers' performance. A fuzzybased model is introduced to assess faculty performance by considering their involvement in various sub-activities within the organization or institution.
The fuzzy Expert System involves several steps, namely Fuzzification, Fuzzy Reasoning, and Defuzzification
During the process of fuzzification, the input variables are categorized into distinct linguistic variables like "Excellent," "Very Good," "Good," "Fair," and "Poor." Subsequently, membership functions are created by assigning suitable ranges to each of these variables. These membership functions can take various forms, such as triangular, Gaussian, trapezoidal, or singleton, depending on the specific requirements.
In this stage, the fuzzy rules are utilized within an inference mechanism to compute the degree of membership of the input to the fuzzy-based output.
Conversion of fuzzy values into crisp values.
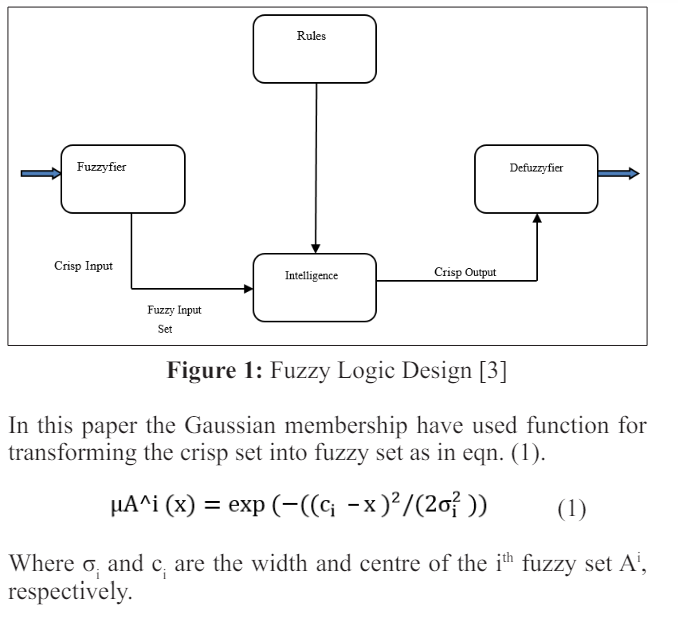
The subsequent sections provide a description of the input and output variables employed in this work, along with their respective linguistic terms.
1. Organization of classes: Faculty's role in organizing and
preparing for classes
2. Punctuality: Timeliness in conducting classes
3. Utilization of teaching aids: Implementation of various
teaching aids by faculty during classroom instruction
4. Effective communication: Proficient communication and
clarification during presentations
5. Supportive learning environment: Creation of a comfortable
and conducive learning atmosphere
6. Student engagement: Interaction with students within the
classroom setting
7. Classroom discipline: Ensuring discipline and orderliness
in the class
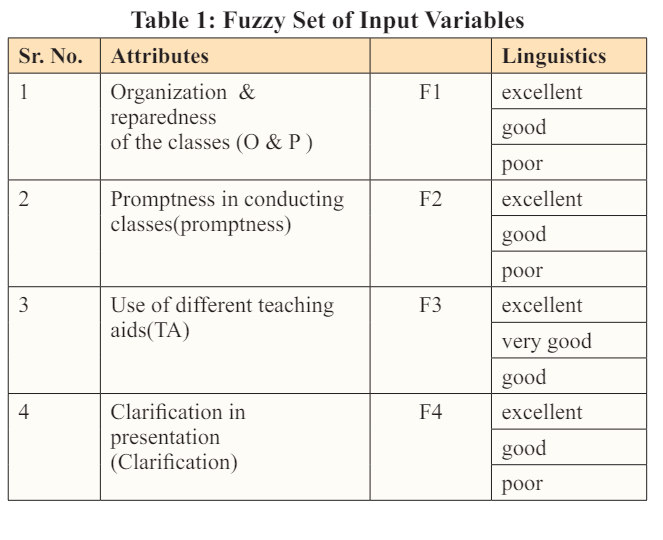
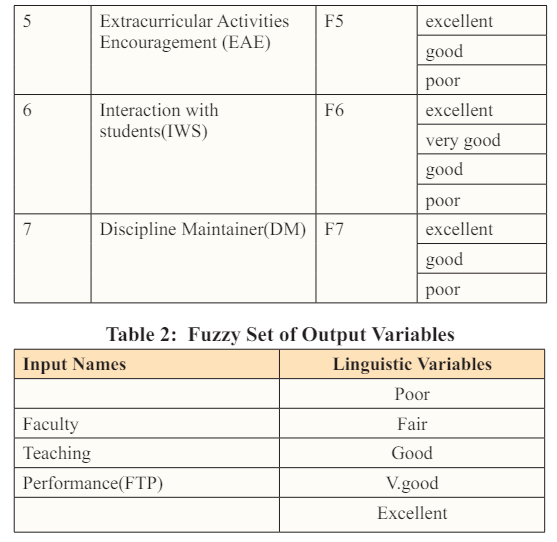
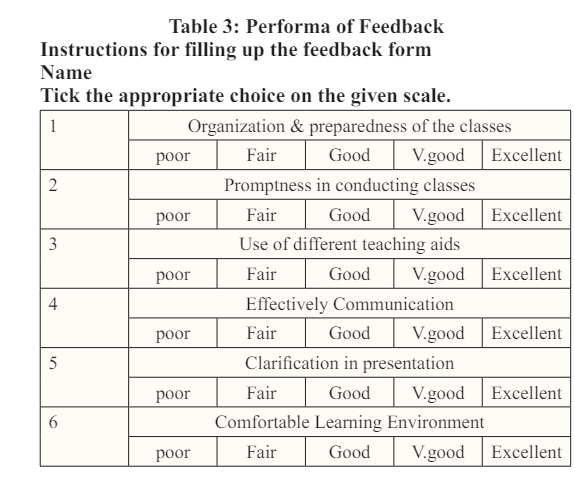
A feedback form, referred to as Table 1, was created to assess the teaching skills of faculty members. The form underwent validation through peer review and incorporated inputs from students via anonymous submission. Only students with a minimum attendance of 60% were eligible to complete the feedback form.
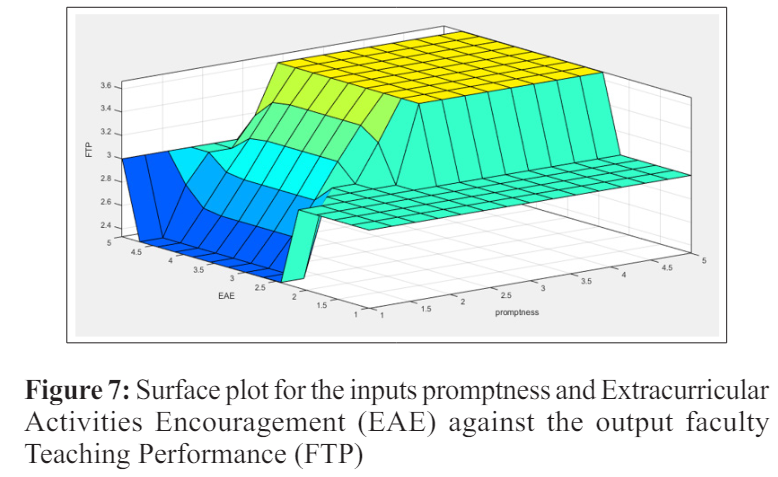
The proposed model was implemented in MATLAB (R2017a) using the Fuzzy Logic Design Toolbox. For this model there are 5 inputs developed, one output Fuzzy Mamdani model as shown in figure 2. The recommended Fuzzy Expert System was tested with feedback of 100 students’ about faculty’s teaching skills which is obtained from an academic institute. The graphical representation of the input and output variables are shown in figures 3-4.


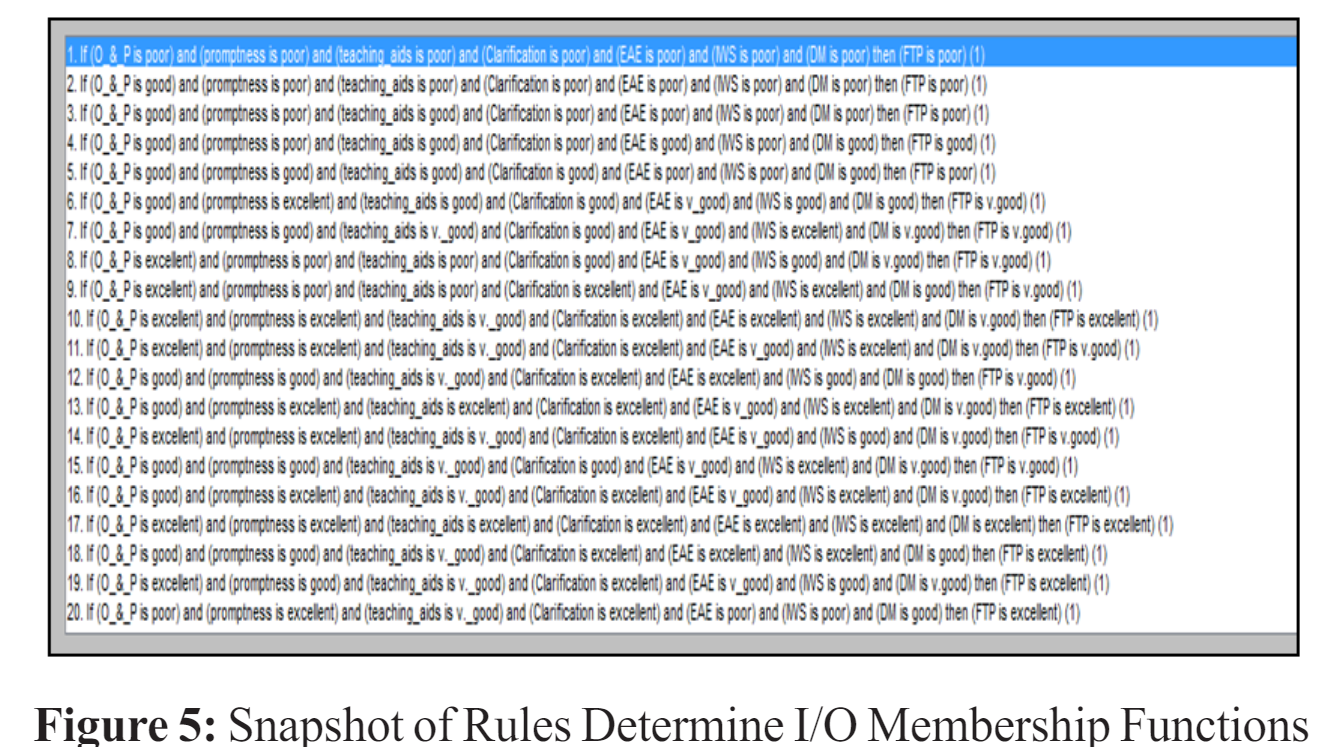
The fuzzy logic controller operates similarly to the human reasoning process through an inference mechanism. It is a subset of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and employs fuzzy logic-based techniques. In evaluating teachers' teaching performance, specific fuzzy rules are defined. These rules establish the input and output membership functions utilized in the inference process. The soft computing model depicted in Figure 1 incorporates a fuzzy logic controller. In this controller, appropriate rules are triggered, and the degree of membership of the output fuzzy variable, which represents faculty teaching performance, is determined by encoding the relevant fuzzy subsets.

To evaluate the model and the defined rules, a dataset was gathered from a well-regarded academic institute for the current study. The collected input data, along with the output variable representing the overall performance of the teacher, were used to determine the faculty's teaching performance using both a conventional method and the developed fuzzy model. The two end columns of Table 4 display the values of faculty teaching performance obtained through the direct method and the Fuzzy Expert System (FES), respectively.


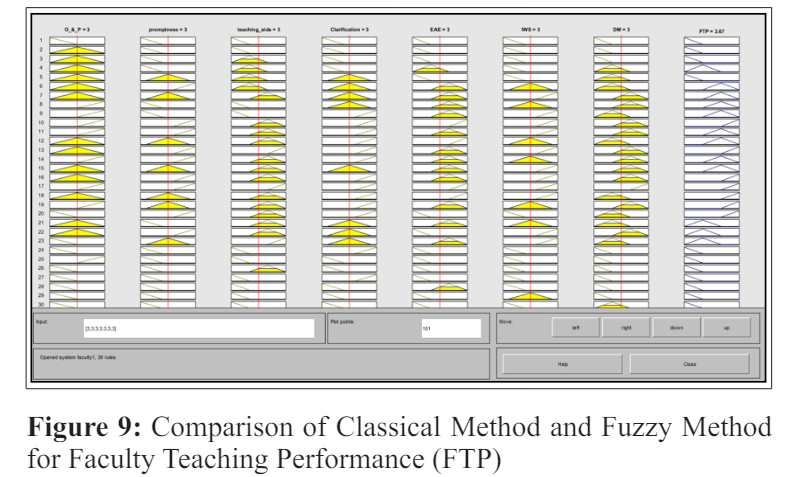
This paper employs Soft Fuzzy Logic Techniques, specifically the Fuzzy Mamdani System, for evaluating faculty teaching performance. Table 4 provides a comparison between the classical method and the fuzzy Mamdani Inference system method for teaching performance evaluation. In the classification method, the feedback inputs are evaluated using the standard mean deviation method.



This paper introduces a Fuzzy Mamdani Inference method for evaluating faculty performance using fuzzy logic techniques. In future research, it would be beneficial to collect additional inputs such as CGPA, overall faculty performance, and examination results to analyze the overall academic performance of academic institutes. Additionally, exploring the combination of artificial neural networks with fuzzy systems, known as Neuro-Fuzzy Systems, holds promise for further advancements in this field and is worth investigating
